The O2O food delivery market in China 2019| Daxue Consulting
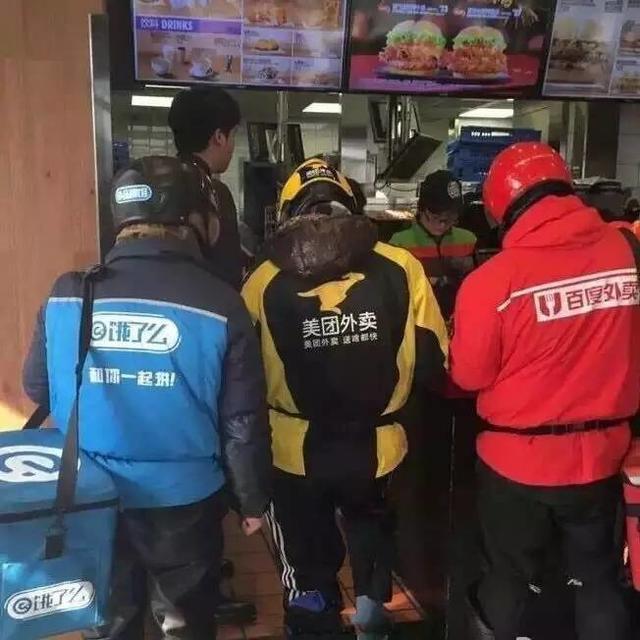
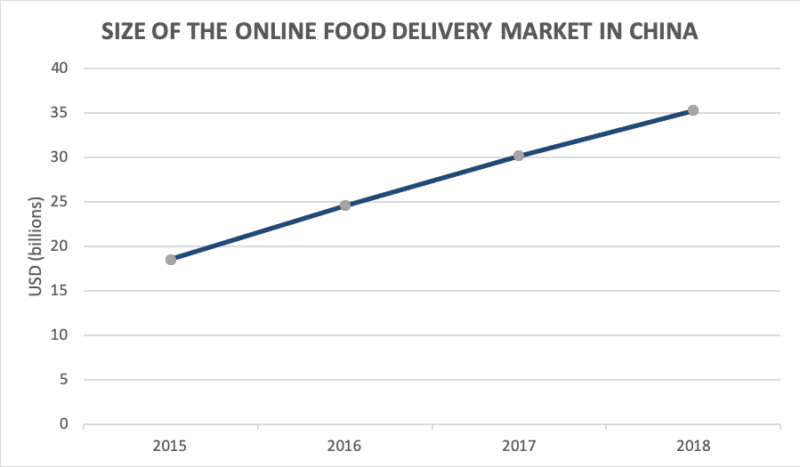
The O2O food delivery market in China is estimated to be worth over 37 billion USD, and it is growing rapidly. Among the products sold online, food is one of the most promising categories: online food sales rose by 36.8% year-over-year in the first two months of 2018. Food delivery apps have an estimated 355 million users, meaning that a quarter of all Chinese people are ordering food from their phones. There are more than 1.8 million food delivery orders placed every day in Beijing alone.
Transformation of eating habits in China
Getting takeout food is a relatively recent phenomenon in the country. The trend started with foreign fast food franchises such as McDonald’s in the 1990s. Homegrown local restaurants, such as noodle houses and those offering regional specialties, followed suit. But it was not until the rise of online food delivery platforms that the O2O delivery market in China took off.
Since 2009, when the first food delivery app Ele.me appeared, the number of customers using these platforms has gone up from zero to 406 million at the end of 2018. Nearly half of China’s internet user base has ordered takeout food through apps at some point in their life.
The development of online delivery has improved the food processing and supply capabilities of offline restaurants. At the same time, it has also stimulated new demands due to convenient and fast services. As of 2020, the growth rate of O2O food delivery market in China is more than 10%. It exceeds the growth rate of the traditional catering industry. Due to the development of diversified consumption habits of Chinese people, the food delivery market in China will exceed 300 billion yuan in 2020.
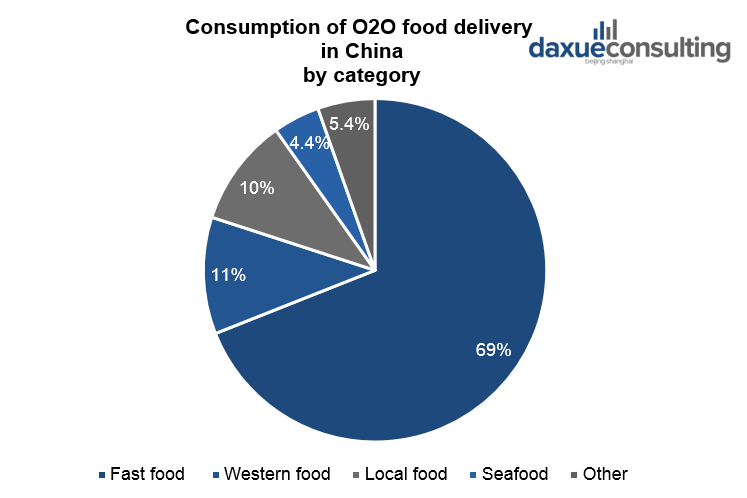
Fast food category dominates in terms of O2O food consumption
In the first half of 2019, fast food accounted for 69% of O2O food consumption. Western food and local dishes had second and third place. Such categories as seafood barbecue, milk tea, desserts also were popular among Chinese consumers when ordering food.
The number of seafood O2O orders increased in 2019
The proportion of seafood in China‘s O2O delivery market increased. It is an important category for night delivery consumption. In the first half of 2019, users consumed more than 150 million seafood barbecues on the Meituan takeaway platform. It had a year-on-year increase of 55.3%. In the first half of 2019, the order volume of crayfish has exceeded 20 million orders. It is about 300 million crayfish.
Semi-prepared food and vegetables as a new trend in the O2O food delivery market in China
Online shopping for semi-prepared dishes has become a new choice for young consumers. This new trend has led to a rapid increase in sales of semi-prepared food. In 2019, 800,000 semi-finished dishes have been sold. At the same time many elderly people have changed their habit of hoarding vegetables for Spring Festival. They started to order home delivered fresh vegetables. Sales on the platform Taoxianda increased 172 percent compared to 2018. “The semi-prepared dishes satisfy young people’s enjoyment of cooking at home,” said Yongcheng, a sales clerk at Tmall.
Penetration rate of the O2O food delivery market in China continues to increase
As the market scale continues to grow rapidly, the penetration rate of the food delivery industry continues to increase. In 2018, the penetration rate was 10.8%. By the third quarter of 2019, this figure had increased to 15.9%.

Breakdown of the O2O food delivery market in China

The food delivery services in China work through apps, which show lists of food providers nearby or allow the user to search for specific restaurants. Clicking on the restaurant brings up the menu and the ordering system, which uses online payments or bank cards. The apps also allow users to rate the food and service, as well as show the location of the delivery driver so an order can be tracked. The apps take about 20% of the order revenues.
The Chinese food delivery industry is high growth and highly profitable, but it is hard for outsiders to enter the space because two platforms control 90% of the food delivery app marketplace.
Who are China’s food delivery industry’s consumers?
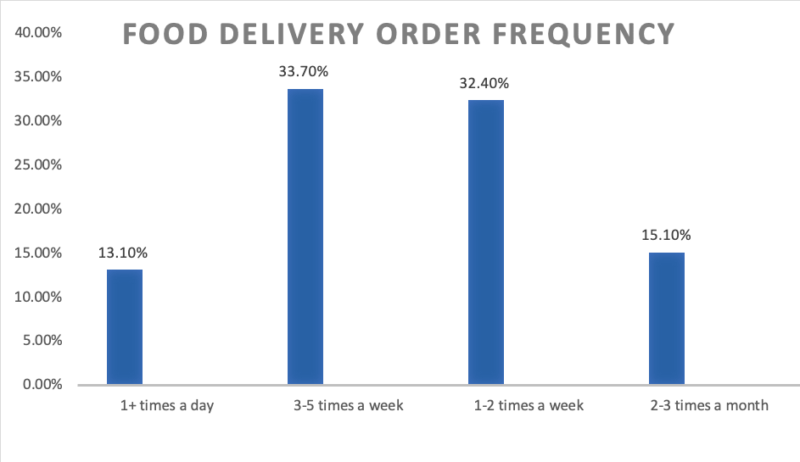
The food delivery industry in China is so large and profitable because of how often consumers make purchases. 256 million people in China used online food ordering services in 2016, and in 2017 that number rose to 346 million. Now it is 355 million. 35% of food-delivery app users order food one to three times a week, and a separate 35% of users order food four to six times a week, according to a report by iiMedia Research.
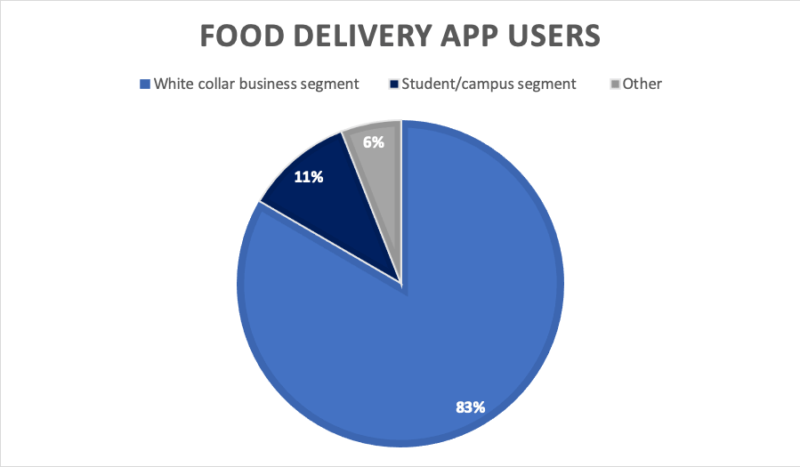
Online food delivery service users are primarily white collar workers. In 2015, about 63% of online food delivery app users were white-collar workers and 30.5% were students. Now, 83% are white-collar workers, and only 10% are students.
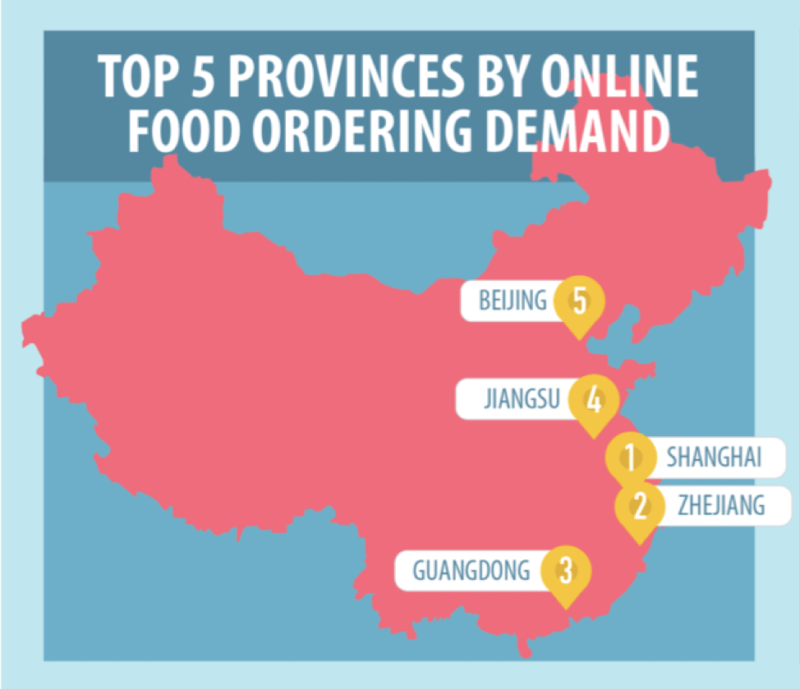
Consumers are clustered in top tier cities, with Shanghai boasting the highest number of users per capita.
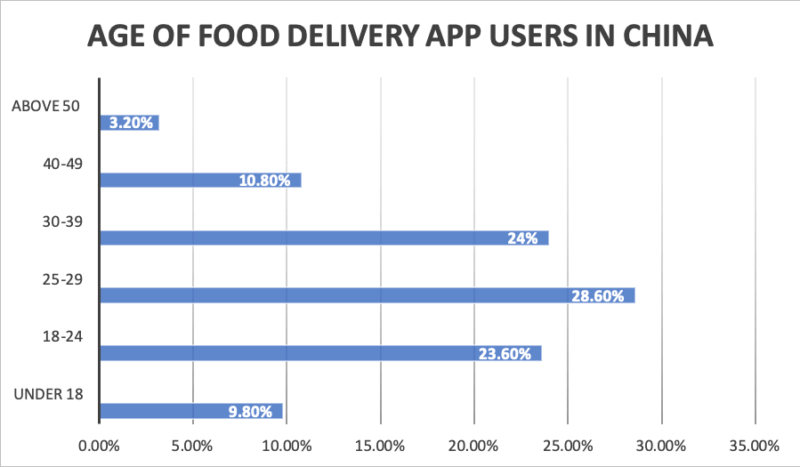
Consumer demographics are split nearly evenly by gender, with women making up 51% of food delivery app users. Users are overwhelmingly young, with 75% between ages 18 and 39.
Contact us for any question on the Chinese market
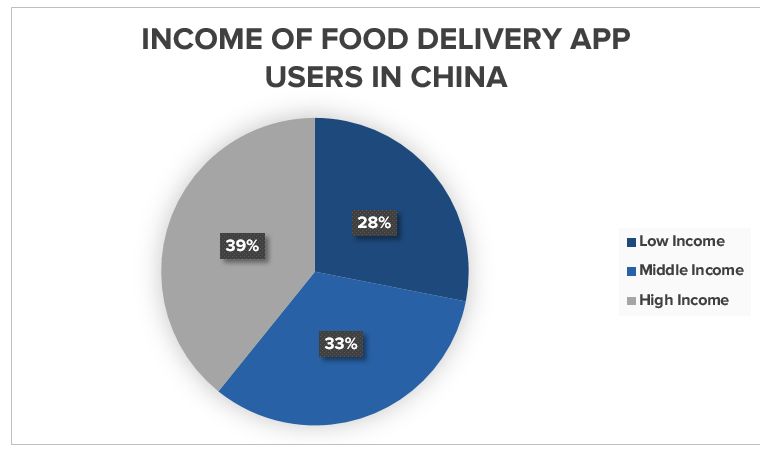
Food delivery in China is popular among all income demographics. Consumers are split nearly evenly by income level, with high-income consumers boasting only a small edge.
Why is food delivery so popular in China?
Because of the intense competition between delivery apps in Great China, consumers often receive steep discounts and coupons when they place an order. This can often make ordering food cheaper than eating it in a house. The intensive couponing practice is a result of price wars between the industry’s two major players, Ele.me and Meituan. The rivalry has hit both companies hard, with Meituan’s operating losses crippling year-over-year to USD 510 million in the third quarter of 2018. Ele.me will also face pressure soon as their parent company Alibaba copes with slowing revenue growth. Coupons are no longer as high as they once were, but consumers still receive them often.
CONTACT US NOW TO ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ABOUT BUSINESS IN CHINA
Meal delivery in the Chinese market is significantly more popular in China than in the West, owing in some part to the fact that food delivery costs in China are about 10% to 20% of what they are in the US.
Which apps dominate the food-delivery industry in China?

The food delivery market is a duopoly dominated by Chinese tech giants Alibaba and Tencent, who own Ele.me and Meituan respectively. Combined, these two delivery apps control a 90% share of China’s food delivery market.
Longtime rivals Alibaba and Tencent have been competing across industries for years, and China’s meal delivery is just yet another sector for them to battle in. The two giants are not just competing for the O2O food delivery market in China, but they are racing to gain new users who can be guided to other Alibaba or Tencent services. Owning Ele.me gives Alibaba a treasure trove of consumer data, and the same goes for Tencent’s ownership of Meituan. Data derived from Chinese meal delivery apps provides insights about consumer spending power, eating preferences, and payment profiles.
Chinese meal delivery app: Ele.me
Ele.me is China’s largest food delivery giant with 53.4% market share. They have 260 million users, 3 million couriers, and are estimated to have delivered nearly 300 million orders. Alibaba in 2018 valued Ele.me at USD 9.5 billion.

Chinese meal delivery app: Meituan Waimai
Meituan Waimai, commonly known as Meituan, controls 40% of China’s food delivery market. Similar to Ele.me, Meituan is an online-to-offline (O2O) food delivery app that provides users with online ordering, food delivery, and some other related services in China. Significantly, Meituan offers more non-food delivery services than Ele.me, such as flowers, office supplies, and more.

Contact us for any question on the Chinese market
What are the benefits/drawbacks for restaurants of being on food delivery apps in China?
Listings on food delivery apps give restaurants in the Chinese market new profit sources, widened service awareness, and new consumers. App operations can be so profitable that some “virtual restaurants” operate out of the kitchen only. However, profit margins for restaurants are declining swiftly. To gain Chinese market share, Ele.me and Didi provided restaurants with subsidies to entice them into selling food on their apps. But as the apps struggle to become profitable, they are raising commission rates on the food providers. Commission rates vary by restaurant location, size, and type, but most restaurants give the apps 20% of order revenues. For restaurants operating on low margins, this can hit hard. To keep profits stable, restaurants must shift the burden to consumers and raise menu prices. Otherwise, they are forced to absorb the new costs – keeping consumers happy but hitting their profit margin hard.
The Chinese food-delivery industry: Looking ahead
Ride-hailing app Didi recently threw its hat into the food-delivery ring, starting in March 2018. Didi provided subsidies and incentives to restaurants and consumers, forcing Meituan to follow suit before local authorities stepped in to demand an end to the “extreme” marketing practices. As Didi expands to other cities, the subsidy battles will likely continue.
Make the new economic China Paradigm positive leverage for your business
Do not hesitate to reach out to our project managers at dx@daxueconsulting.com to get all answers to your questions