The venture capital market in China: Could the Coronavirus eventually revive startup investments?
From the late 80s, China has demonstrated success in transforming its economy from being factory-driven into innovative-driven. This has been occurring together with the government’s strong financial support to position the country at the forefront of technological innovation. The ‘Torch Program’ represents the keystone of this strategy, being the catalyst for startup investments in China. If 2018 marks the climax of the Venture Capital (VC) market in China, 2019 witnessed a dramatic decline. Investors had become more cautious regarding their tech investments in China.
Come 2020, the Coronavirus crisis acted as a game-changer for the entire industry. Nurturing disruptive innovation, and highlighting the most promising startups, could this virus eventually stretch back fundraising activities in China?
A brief History of startup investments in China
The history of Venture Capital in China begins long before one could imagine for a state with communist underpinnings. Yet, the late 1980s already saw private investment take off, thanks to reforms and new programs launched together to stimulate the Chinese economy.
The ‘Torch Program’ has been the launchpad for China’s high-tech revolution
In 1988, the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) launched the ‘Torch Program’, aimed at developing high technology and achieving industrialization. The program established high-tech industrial development zones across the country, gathering scientific and technological resources, as well as talents and money. These high-tech zones include three major parts:
- Science and Technology Industrial Parks (STIPs) to develop the commercialization of emerging technologies and research. China set up 54 STIPs, which accounted for close to 50 percent of all of China’s R&D spending.
- Productivity Promotion Centers (PPCs), incubators designed at providing consulting and product testing services.
- Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) support the growth of Chinese startups by providing incubation services, such as free office spaces.
Torch truly enabled China’s high-tech revolution by being critical to the growth of large international tech companies such as Baidu, Lenovo, ZTE, Alibaba, and Huawei. According to Steve Blank, one of the first to write about the rise of China’s VC market, “of all the Chinese innovation programs, Torch is the one that was run like a startup – iterating and pivoting as it learned and discovered. This enabled Torch to evolve with China’s rapidly global economy.”
Output’s estimations of the Torch Program display the importance of Torch parks as an engine of Chinese technology in the economic growth of the country. Thus, the initiative is responsible for 11% of China’s GDP, and more than 10% of China’s industrial value.

[Source: LinkedIn, The ‘Innoway’ incubator of Zhongguancun Science Park, the first STIP to be established, in the suburbs of Beijing]
Seed funding in China brings capital for early-stage startups
Even if the Torch program enabled startups to access financial resources (by 1991, 70 percent of them received bank support), those were generally at a later stage of development. To bridge the financial gap for early-stage startups to access larger investments, the State Council launched the Innovation Fund, known as ‘Innofund’. This initiative provided small and medium tech companies with capital raised from local governments, banks, investors, and enterprises. By 2014, the found backed more than 30,000 Chinese tech startups, allocating over RMB 19 billion ($2.7 billion) to kickstart early-stage projects.
State-sponsored venture capital funding to support state-owned companies
Since the mid-1990s, the Chinese government extensively encourages investments in technology and IT infrastructure. Innovation became one of the only areas in which the government allows venture investments, with state-sponsored VC funds becoming a popular way for local authorities to finance projects. These government-backed funds were meant to invest primarily in state-owned companies with the goal of increasing quality standards to compete with international companies.
To attract even more capital into technology startups, the MOST launched the first of many state-owned ‘guidance funds,’ in 2007. The fund invests in VC funds in targeted sectors of interest, as well as co-investing alongside other VC firms. In 2018, there were more than 2,000 operating guidance funds, with total funding reaching RMB 5.3 trillion ($790 billion).
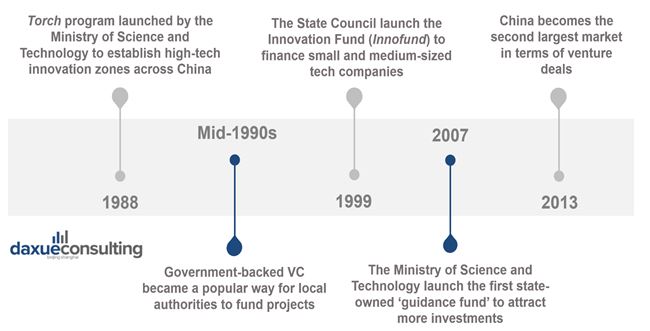
[Daxue Consulting – The history of the VC market in China]
Foreign investment in China represents a third of China’s venture capital investments
In 2018, foreign VC funds contributed to more than 30% of startup investments in China, most of them using USD to raise funds. Nonetheless, an increasing number of these foreign VC firms are now considering raising funds in China using its local currency, Renminbi (RMB). Since the 2010s, RMB funds are becoming increasingly attractive to foreign investment in China. Thus, non-RMB funds are not currently allowed to exit via IPO on domestic exchanges, an option only made available by RMB funds. Overall, local-currency funds benefit from less regulatory supervision and greater flexibility regarding the sector of investment.
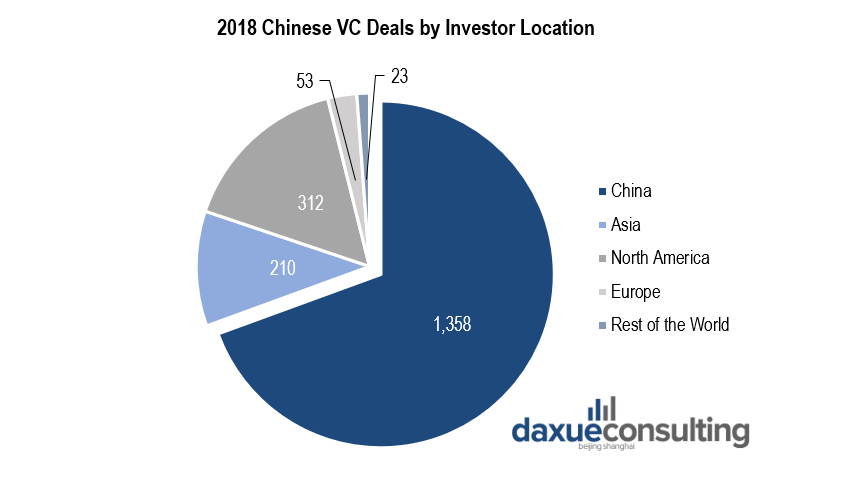
[Data source: Pitchbook, 2018 Chinese VC deals by investor location]
How innovation and Chinese tech giants shape the Venture Capital market in China
China’s VC market has seen a dramatic rise over the past five years, heavily relying on robust financial infrastructures. A strong regulatory system, open market, and the diversification of ways of exiting build this financial pedestal. Aside from this trend, the distinctive growth story of the tech investments in China can be explained by the two following trends:
Entrepreneurship promotion and innovative ecosystem
In 2014, Premier Li Keqiang introduced the principle of “Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation” to support the development of innovative startups. Since this announcement, the government has created favorable conditions for the development of micro-companies. Tax Incentives for Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation cut the corporate income tax of small businesses by half, and days required to start a business in China have considerably fallen from close to 30 down to less than 9.
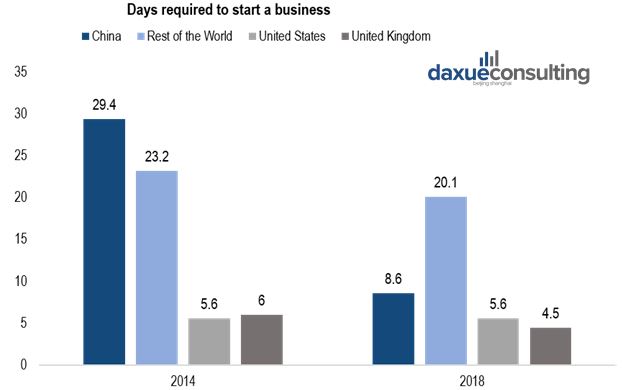
[Data source: World Bank, how long it takes to start a business around the world]
According to the Global Innovation Index (GII), China is gradually closing the gap with other highly innovation-skilled players such as Germany and the United States. The country leapfrogged from the 26th place in 2016 to the 14th in 2019. The index lists knowledge and technological output as the first area of capabilities of China to thrive into global innovation. With 7.4 million university graduates in 2017, China has boosted the number of students qualified for higher education. In 1997, only 5.5% of college-aged students were enrolled in universities, against 55% in 2017. This growing educated population represents a significant pool of knowledge to nurture research and technological outputs.
If capital such as R&D expenses is commonly regarded as the driving force behind scientific innovation, startups born from theses researches foster Venture Capital firms that seek return on investment from these highly promising new-born companies. From the 1980s, capital injected to promote entrepreneurial spirit and build an innovative ecosystem of incubators eventually enabled the Venture Capital market in China to bounce in recent years.
Unicorn startups in China
The intertwined links between the growth of an innovative technology ecosystem and the Venture Capital market in China can be assessed through the number of unicorn startups in China. These privately held startup companies with a value of over $1 billion represent an indicator of the degree of implication of both VC firms and tech startups in the Chinese innovation landscape.
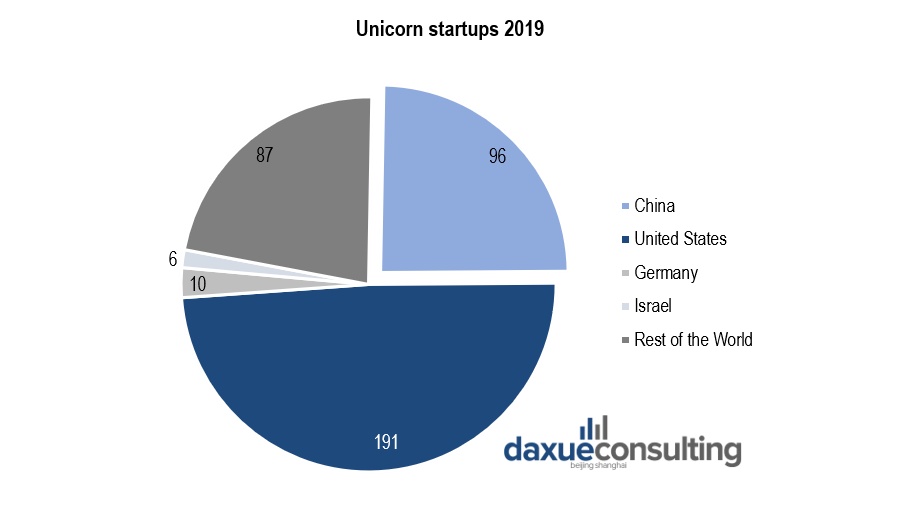
[Data source: Deloitte, Location of Unicorn startups in 2019]
Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent: Venture Capitalists gluttons
Chinese tech giants, known by the acronym BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent) dominate the Chinese consumer journey, providing an extensive range of services that cover every segment of daily-life activities. Initially, each of these companies started with a single business. Baidu provided an internet search engine, Alibaba was a B2B marketplace, and Tencent was a messaging application. As Chinese consumers quickly embraced mobile internet technologies, BATs rapidly expanded their strategies to meet consumer needs.
As BATs want to capture every minute of the day’s availability from Chinese consumers, they represent a significant investment force in startups in China. They invest through their corporate funds, a practice called Corporate Venture Capital (CVC). According to Pitchbook, the top three technology companies in China had made more than 920 Venture Capital investments by 2018. Importantly, the Minister of Science and Technology has publicly stated his strategy to use BATs to accelerate the country’s leadership in three strategic sectors: Baidu oversees accelerating autonomous driving, Alibaba the smart cities, and Tencent the computer vision.
The government’s involvement in BATs’ strategic axes and their investments echoes the multiple funds-of-funds that have accompanied tech investments in China since 2007. For example, BATs have invested in nearly a third of Chinese Unicorn startups. Recently, Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent all invested in the rise of the short video apps lead by ByteDance.
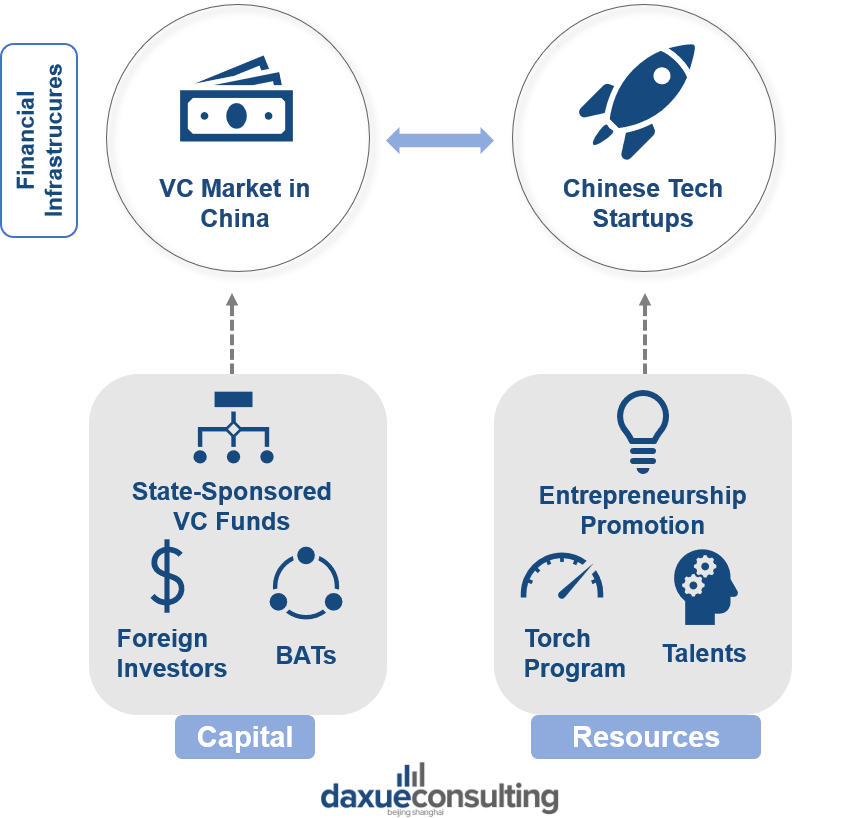
[Daxue Consulting – The mechanisms behind the Venture Capital market in China]
The ‘capital winter’ was there before the Coronavirus
The venture capital investments of the past five years fostered a new generation of startups, from Tiktok’s parent company ByteDance, to the ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing. 2018’s forecasts about the Venture Capital market in China were still predicting the trend to keep its growth pace towards more deals backing the Chinese startups. However, after five years of exponential growth, the trend is now reversing.
The second quarter of 2018 marks the peak of tech investments in China, with digital-payment giant Ant Financial closing a record US$14 billion deal. In the meantime, lifestyle-services giant Meituan-Dianping raised US$4 billion, while Q1 saw Didi Chuxing secure a US$4.6 billion investment. By comparison, 2019 Q2’s largest venture deal was a $1 billion investment in JD.com’s affiliate healthcare branch.
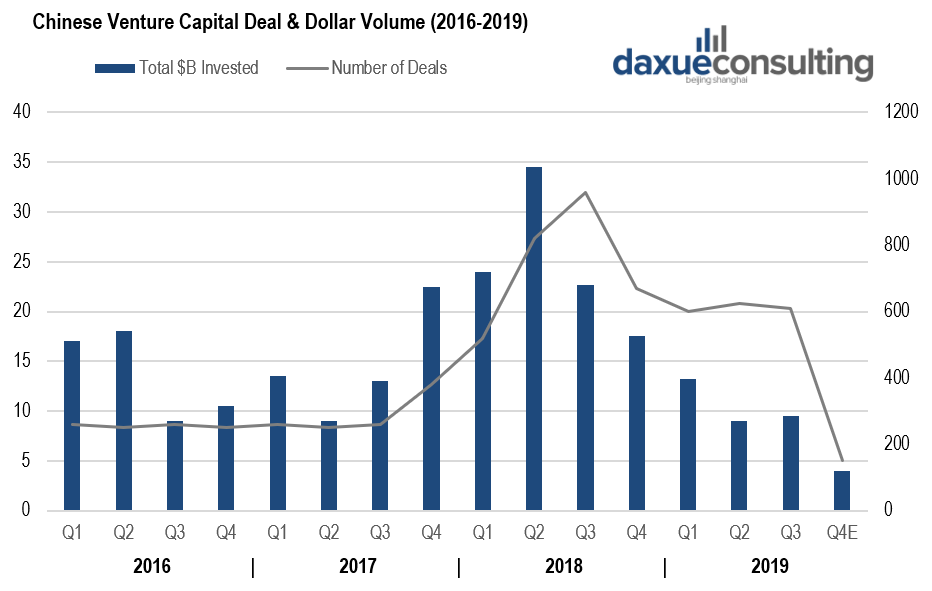
[Data source: Crunchbase, 2016-2019 Chinese VC deals, and dollar volume]
The tech investments in China plummeted from US$93.8 billion in 2018 to less than US$40 billion in 2019, evidencing the ‘capital winter’, which defines a significant slowdown in fundraising and investment activities. As China increasingly positions itself as the engine of global innovation, which factors precipitated the winter for the Venture Capital market in China?
Investors are becoming more cautious than ever
Alexandre Dorangeville, vice-president at Rochefort & Associés, a cross-border investment bank, told Daxue Consulting the VC market in China is likely to come at the end of a cycle.
“Some companies – Ofo, Luckin Coffee are the classic cases – displayed the ability to burn cash without showing any ability to become profitable.” 2018 set the expectations of the investors very high, and the results have not yet come up to the desired outcomes. Additionally, poor post-IPO performances of several Chinese tech companies, including electric car maker NIO and smartphone manufacturer Xiaomi achieved to undermine investor’s confidence.
However, the sector is far from depressed. Financial data provider company Preqin estimates the amount of capital waiting to be deployed of Asia-focused Venture Capital firms to be about $95 billion. It is not the shortage of money, but rather that investors are more critical and selective. As a sign that investors behave less risk-taking, Bruno Bensaid, angel investor at Shanghaivest, observed that early-stage startups have been hit the hardest.
Trade War worsens the general economic downturn
The trade war and the general slowdown in the Chinese economy also affected startup investments in China. In 2019, the U.S. government blacklisted a swath of Chinese tech companies, including telecommunication giant Huawei, and the Alibaba-backed AI startup Megvii. As the United-States remains a hot choice for Chinese startups to exit via IPOs, the trade war affects foreign investment in China, who have limited exit options. Another blacklisted company, the most valuated AI Chinese startup SenseTime, was reported scrambling to survive after losing access to U.S semiconductors, necessary for the continuity of its operations.
On the bigger picture, the development perspectives of Chinese startups are intrinsically linked to the country’s economy. However, it is showing clear signs of deceleration, with a historically low level of growth.
Assessing the Coronavirus impact on tech investments in China
While the Venture Capital market in China relies primarily on meetings between investors and co-founders, travel restrictions froze the entire industry. As a result, the number of deals during the Coronavirus drop-off to nearly zero during the last two weeks of January 2020. Instead of canceling its meeting with 30 startups, Sequoia Capital China decided to organize an online pitch contest during the quarantine.
The Coronavirus impact on startup investments in China pushed the ongoing trend towards further caution, said Dorangeville. According to him, assessing the impact of the crisis on the portfolio is the immediate task for investment funds to carry out. “The teams are currently focusing on existing assets and redirecting their cash to portfolio companies to ensure their survival, rather than investing in new deals.”
In the first quarter of 2020, we saw the first contraction of China’s economy in more than forty years. According to data published on April 17, 2020, by the National Bureau of Statistics, the GDP officially plunged by 6.8% compared to the first quarter of 2019.
Thus, the winter could be longer for tech investments in China.
Changes in consumption and tech advancements from the Coronavirus in China
During the epidemic, more than 20 province’s government worked with technology companies to build AI solutions to the Coronavirus in China to report epidemic related data and feedback, providing invaluable advice for public crisis management of priority populations. Part of the tech advancements from the Coronavirus in China, we reported the deployment of disinfection robots in hospitals, big data-powered QR codes and smart image reading systems.
Even if the Coronavirus created a fertile environment for AI, big data, and robotics developments in China, it is not likely to foster a new breed of highly promising startups. Indeed, tech advancements from the Coronavirus in China responded to a specific demand to contain the outbreak.
However, results from Daxue Consulting’s analysis during the Coronavirus show great changes in Chinese consumers’ habits. According to Daxue Consulting’s report, more than 70% of the Chinese tried at least one new service for the first time. The highest are online learning and working from home apps, followed by live streaming and online diagnosis. These online services are will likely keep a strong growth, with 73.6% of people saying they will continue to use it online after the epidemic.
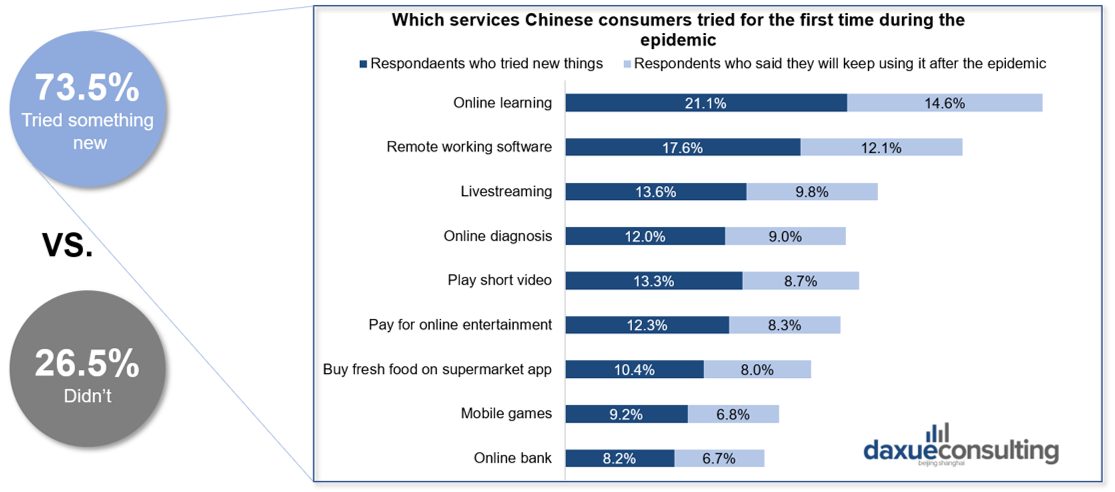
[Data source: Daxue Consulting research, changes in Chinese consumer behavior after the Coronavirus outbreak]
As far as the Coronavirus created a boon for innovation in China and new habits of consumption, does it necessarily mean new opportunities for startup investments in China?
Could Startup investments in China eventually bounce back?
According to Pitchbook, there were 66 deals for the week ending on March 28, 2020. This is the most of any week so far this year and just below the figures from the same time last year. Online learning gaining the most traction from the Coronavirus, Chinese online education startup Yuanfudao managed to raise US$1 billion.
Dorangeville said the post Coronavirus impact on startup investments in China is likely to see Corporate Venture Capital –BATs’ funds being the largest ones on the Chinese VC market – taking the opportunity to close exclusive deals. CVCs in China have a longer-perspective in their investments and the cash available to look at current deals. They will therefore be better able to restart bargaining at low prices by being one of the only sources of financing for the Chinese startups.
“However, this will only be the immediate impact of the Coronavirus,” says Dorangeville, “On the long-run, I think that the 2019 trend will be reinforced after the Coronavirus crisis: investors in China will be even more cautious, taking distance with cash-burning business models and being more active in their post-investment portfolio management companies.”
Author: Maxime Bennehard
Listen to 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast










![[Podcast] China paradigm #6: How to get China’s largest companies behind your tech startup](../wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Daxue-consulting-_-China-paradigm-_-Shuyang-Cao-from-Malu-Innovation-150x150.jpg)




