Fast-Food market in China
Substantial growth of Fast-food market in China by 2016
The Chinese fast food market has experienced strong, consistent growth in recent years. This growth of revenues is predicted to continue from $36.2 billion in 2011 to $107.1 billion in 2016. The market is forecast to have a value of $65,652 million and a volume of 107,126 million transactions. The compound annual growth rate of the market in the period 2011 – 2016 is predicted to be 6.7%
Increased western influences in China and higher incomes have seen increased demand for fast-food. There are constant rapid development of fast-food service providers, improvements in chain store and franchising management, and new brands and food styles. The growth of the market will remain dynamic due to the intensity of market conditions and fierce competition driving expansion. Consumers’ fast-paced lifestyles and demand for convenience and take-away, particularly at breakfast, will push sales of the overall category. Set meals at peak lunch-times have been a dominant feature in the category and create highest value for fast food players.
Five forces analysis of China`s fast food market
Barriers to entry China`s fast food market are low, particularly for independent operators because they do not utilize standardized equipment for their small-scaled businesses. While enterprises engaged in chain/multi-establishment operations may find higher barriers to entry, the reasons of which involve investment on standardized equipment, advertisement, nice decoration and trained waiter. However, entry to this industry can also occur through a franchise agreement. The number of franchisees has quickly increased along with the improved legal framework. This way could largely help to reduce enterprise`s burden.
The main source of buyer power is the lack of switching costs. A consumer`s choice of fast food provider is purely a matter of personal taste which may vary from one day to another. Whatsoever, despite signs of saturation, investment in this sector has been rising. Investment in branding keep attracting new customers while the extreme convenience of fast food makes it still important to the consumer than simple source of food. Buyer power is at medium level.
As for supplier power, it is important to save cost through maintaining reliable suppliers offering food of marketable quality with low margin and high volume. Food suppliers may also have customers in other food service sector. So they have strong bargaining power. Despite the minimum wage legislation, fast food store holders can employee students to do part-time jobs. This helps to save cost on labor supply.
Substitutes for fast food include other forms of profit foodservice as well as fresh food and spicy retail for home cooking. As convenience and availability are the main drivers for consumers` choice for fast food. Even though there are home convenience food in supermarkets, the switching cost is the opportunity cost of the time spent in the kitchen and that the taste of food may be not as good as that in a fast food restaurant.
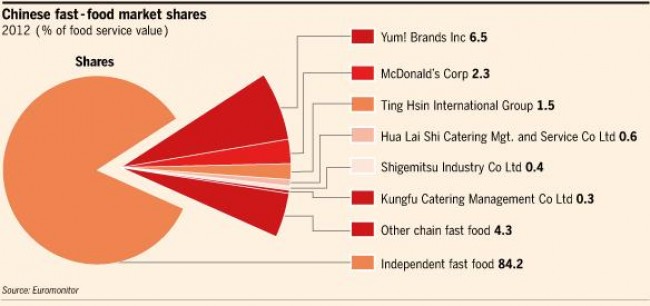
In terms of degree of competition, as some particular segments of the fast food market is concentrated, for example, the fairly-fragmented burger market, the rivalry has been enhanced. Chinese style fast food still occupies a majority in market shares. The main competitors of overseas new entrants in fast food sector are not KFC or McDonalds but Chinese brands and street vendors. There is a trend towards organization among domestic players, which are more and more looking at expansion and developing their brands, with some of them even offering Western-style food, albeit at a cheaper price point than the internationals. In response, KFC China opened “Dong Fang Ji Bai” offering specially designed fast food with Chinese flavors.
Several big foreign players, accounted for almost 16.8% in China are McDonalds, KFC, Burger King, Pizza Hut, Domino`s Pizza, which used to attract mid class in late 1990s and 2000s, but now are visited by more new citizens from countryside and the young, while growing health concern among middle class make them turn to higher end food service providers.
It is estimated that there will be more than 10 big brands in China In the next decade. The great opportunity in fast food industry will be supported by the expansion of Chinese cities and the quick speed of daily life. The concept “quick” will be a key to success. Less waiting time, quick food processing and warm environment will be the selling point. As a large part of Chinese catering industry is lacking sufficient management vision and skills, standardization and good management of cost, pricing, service quality and branding will be a core competency for new entrants to the markets.
Amy Wang, business consultant China
Euromonitor / IBTimes / China.org