China’s ambitious artificial intelligence vision | Daxue Consulting – Market Research China
China has embarked on an unprecedented effort to master artificial intelligence. AI is an important facet of Beijing’s ‘Made in China 2025’ blueprint. Supplementary to this endeavor, in 2017, China published its “Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan” (新一代人工智能发展规则) which laid out China plans to become the world leader in artificial intelligence, with a domestic AI industry worth almost US$150 billion. Thus, China’s sweeping vision for global AI ascendancy has resulted in an extraordinary monetary and policy commitment from the government. On top of this national level led investment, the country’s top tech companies, led by the Internet giants Baidu (百度), Alibaba (阿里巴巴), and Tencent (腾讯), are currently nurturing large levels of talent and expertise in artificial intelligence, building new research hubs for innovation and development, and investing into capabilities to develop these technologies to rival those operated by Amazon, Google, Facebook, and Microsoft.
China has some big advantages in AI. For one, it has a wealth of talented engineers and scientists. It also is rich in the data necessary to train AI systems. With fewer obstacles to data collection and regulations on widespread usage, China is amassing huge databases that don’t exist in other countries. The results can be seen in the growth of facial-recognition systems based on machine learning: that now identify workers at offices and customers in stores and authenticate users of mobile apps.
The future of artificial intelligence depends on the conjoined evolution of the algorithm and the data to best accommodate the needs in production enhancement. Thus, China has enacted a three-step plan in the advancement of its artificial intelligence initiatives: firstly, it must be able to keep pace with all leading AI technology by 2020. Part two is to make major breakthroughs by 2025 in medicine, city infrastructure, manufacturing, agriculture, national defense, construction, and insecurity and control assessments. And part three, to establish China as the world leader in AI by 2030.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
By definition, Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that emphasizes the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans. Artificial intelligence (人工智能) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs, and perform human-like tasks. Most AI examples that we hear about today, from chess-playing computers to self-driving cars, all rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing. Using these technologies, computers can be trained to accomplish specific tasks by processing large amounts of data and recognizing patterns in the data. Early work in artificial intelligence paved the way for the automation and formal reasoning that we see in computers today, including decision support systems and smart search systems that can be designed to complement and augment human abilities.
Nowadays, examples of AI design and use include speech recognition, learning, planning, and problem-solving. However, research associated with artificial intelligence is highly technical and specialized. The core problems of AI that still remain prevalent today include programming computers or machines to possess certain traits such as knowledge, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, learning, planning, and the ability to manipulate and move objects. However, it is widely acknowledged that initiating common sense, reasoning and problem-solving power in machines is a difficult and tedious task. This aspect of AI will remain a challenge in the following years for the top innovators in the field.
AI excellence in China: The Big Three – Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent

Chinese Vice-Premier Liu He speaks at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference in Shanghai (Source: Reuters)
At this year’s World Artificial Intelligence Conference in Shanghai, the government announced that AI projects and platforms will be offered financial support of up to 100 million yuan. In addition, AI enterprises will be granted further access to data resources in areas including education, health care, and tourism. These announced measures signify Shanghai’s efforts to promote the AI industry in China with a particular focus on attracting more talent, capital, and to optimize the use of big data. “Shanghai needs to seize the opportunity that the AI industry has created, and take full advantage of the city’s abundant resources in scientific research, talent, data, and policy support to implement more new AI technologies,” said Ma Chunlei, deputy secretary-general of Shanghai municipal government. Thus, we can see that the AI industry in China is being propelled forward on all fronts and has become a hot buzzword within the broader society today. The government is in the process of laying the base for a new Chinese economy with AI integrated into transportation, financial services, retailing, agriculture, eco-friendly manufacturing, health/medical care and many other applications.

Xinhua’s first English #AI anchor makes debut at the World Internet Conference that opens in Wuzhen, China. (Source: Xinhua
Furthermore, the top industries in China to be disrupted by AI are autonomous vehicles, online and offline commerce, financial technology, and healthcare. Baidu and Didi Chuxing are leading the former category with their advanced self-driving technologies, Alibaba the second category with a greater focus on using AI to enhance product personalization and customer service. Regarding the last two, China’s Fintech startups using AI to improve security in ID authentication, and in healthcare, with startups using AI to provide computer-assisted medical diagnoses.
Specifically, Baidu chief executive Robin Li Yanhong noted the Chinese government’s supportive state and industry polices as major factors contributing to the rise and success of his internet company and the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in China. Beijing-based Baidu operates China’s dominant search engine and has pushed into artificial intelligence, notably in autonomous cars where it is striving to build an open-platform for self-driving car technologies. Baidu is also part of a group of five companies including Tencent, Alibaba, iFlyTek and SenseTime, tasked with building “open innovation platforms” in their respective fields. Baidu’s focus is on autonomous driving, Alibaba’s cloud computing division is tasked with a smart city project to improve urban life, while Tencent’s focus is on computer vision for medical diagnosis. iFlyTek, a dominant player in voice recognition, is tackling voice intelligence and SenseTime is working on intelligent vision.
Thus, we see that AI has a major role to play in transforming healthcare, agriculture, and education where AI will help find better cures for diseases, democratize access to healthcare, improve crop yields, and help personalize education for all. AI is also likely to boost traditional industries like telecom, retail, advertising, automotive, business services, and the consumer market. The public sector is also expected to be one of the biggest beneficiaries of AI in the Asia Pacific region, helping cities leapfrog their Western counterparts in terms of smart intelligent services and improved standards of living.
China is attracting AI investments worldwide
The Artificial Intelligence market in the Asia Pacific region as measured in 2017 is expected to grow from $6 billion dollars to $136 billion by 2025. Below shows the size of the artificial intelligence market in China from 2015 to 2020. China’s AI market was worth 23.74 billion (US$3.55 billion) yuan in 2017, up 67 percent from the year before, with computer vision, voice, and natural language processing accounting for most the market. It has been estimated that China’s AI market will grow 75 percent in 2018 and is forecasted to grow to around 10 billion U.S. dollars in 2019.
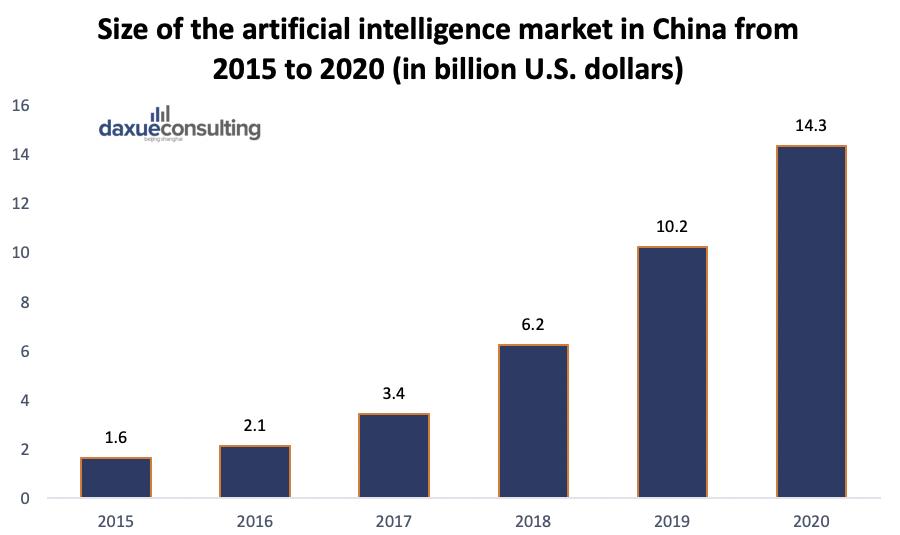
Sources: China Money Network, Statista estimates 2018
Two-thirds of global investment in artificial intelligence is being allocated towards the Chinese AI industry, which alone has helped the AI industry in China grow by 67% last year alone. China Money Network, a leading source of information on China’s technology sector, recently announced in a report the top 50 AI companies to watch. In this report, they included 14 “unicorns,” i.e., start-ups with a valuation of $1 billion or more, totaling an approximate monetary worth of $40.5 billion. With the Chinese government heavily backing many of these companies, it is hoping that artificial intelligent uses will reach a domestic valuation of 1 trillion yuan ($146 billion) by 2030.
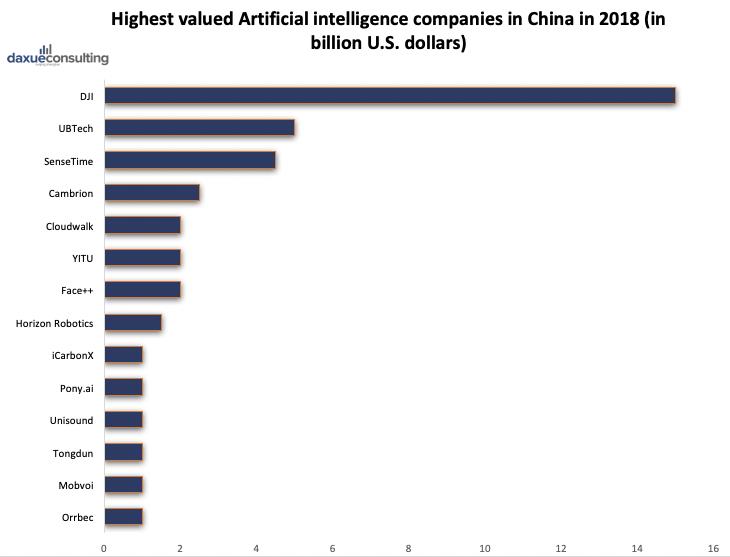
Sources: China Money Network, Statista 2018
Thus, with recent initiatives to improve China’s in-depth knowledge and better understanding in artificial intelligence along with a high level of prospective growth in the industry, China has become one of the most attractive markets for attracting AI investments worldwide.
Lastly, another reason why this industry is so significant is due to artificial Intelligence projecting to have a profound impact on the future GDP growth in China. By 2030, Artificial intelligence is forecasted to enhance the gross domestic product of Chinese energy, utilities and mining industries by 11 percent in terms of productivity. For the consumer goods, accommodation and foods services, as well as in the TMT, financial and professional services, AI will enhance these sectors’ contribution to the total GDP of China by 30 percent respectively. What this means is there are tremendous opportunities for higher access to research and development in the field of AI along with a plethora of AI-powered technologies across all industries. Thus, for foreign firms looking to abstract this emerging resource and to access these burgeoning technological localities along the east coast of China, China presents a golden opportunity for AI-based collaboration and innovation in the products and services.
How is Artificial Intelligence used in China?
Health in China
The medical fields have been one of the primary benefactors of AI-based technologies as well as one of the first industries to embrace AI. One of China’s leading AI startups in health is Infervision, an artificial intelligence high-tech company committed to applying deep learning technology to assist medical image diagnosis as efficient and accurate solutions. Infervision effectively uses various types of medical data to create clinically valued products and promotes precision analysis in the medical field especially in assisted image diagnosis. Based on years of research preparation, they launched the world first artificial intelligence precise healthcare platform and is the first to release intelligent X-ray assisted diagnosis products and intelligent CT assisted diagnosis products. These products are already in trials at Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Tongji Medical College of HUST in Wuhan, and Dalian Zhongshan Hospital.
The company is also engaged in academic research and has established a deep cooperative relationship with top institutions in Chinese Radiology, combining both medical science and medical technology while laying a solid foundation for artificial intelligence breakthroughs in the medical field. Infervision has established cooperative business partnerships with close to 20 Tertiary Grade A hospitals and has successfully broken the barriers between medical data, technology, and application scenarios in China, creating a unique system of an artificial intelligence computing platform and precise healthcare intelligence system.
Driverless-vehicles in Mainland China
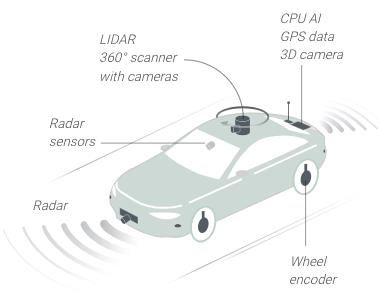
Although China possesses the world’s largest car market – both for conventional and electric vehicles – it still lags behind the US in terms of developing driverless vehicles for the road. For this industry component, the Chinese government has set the goal of having a manufacturing industry in place for sensors and embedded chips with a value exceeding the US $1.4 billion dollars by 2020.
An example of the practical application of artificial intelligence in this industry can be witnessed through the Chinese company Didi and its innovation motives to “Revolutionize the World’s Transportation and Automotive Technology through machine learning.” With the tremendous amount of data Didi collects every day, they are in a unique position to tackle traffic congestion and optimize navigation routes with AI technology. They launched the Didi Smart Transportation Brain that combines video camera and sensor data from Didi’s cars with data from the government and other partners. The objective is to create a city traffic management system powered by AI and cloud technology. The idea is that this will ultimately will result in smart traffic lights and monitoring systems that can be used in any metropolis with road congestion.
Furthermore, new technologies to enhance the rider’s experience such as an app-based augmented reality (AR) navigation service that helps passengers find their way through buildings, malls and train stations to reach a vehicle pick-up location, illustrate Didi’s dedication to remaining the transportation leader in China. In cars, a voice-activated digital assistant offers a wide range of services including audio and video content as wells as locations for fuel, recharging or repair services.
Computer-chips in China
China makes more than 90 percent of the world’s smartphones, 65 percent of all personal computers and 67 percent of smart televisions. However, the country relies on imports for most of the chips in these devices, valued at the US $260 billion last year. This facet outlines perhaps the biggest gap in China’s AI arsenal and explains this year’s move by the big Chinese tech companies into hardware. Specifically, Baidu, Huawei and Alibaba are among those working on building their own AI chipsets, with the e-commerce group spearheading a drive into quantum computing. Alibaba wants to have its first artificial intelligence chips on the market next year, although there remains ample skepticism over these companies’ ability to accelerate development in the field. For now, the chips driving much of China’s AI are from US chipmakers such as Qualcomm or Nvidia, including the software being largely foreign in origin.
In contrast, however, the Financial Times recently reported that Horizon Robotics, one of China’s leading designers of artificial intelligence chips, is raising up to $1bn in a funding round that will value it at between $3 and $4 billion. The three-year-old company, which is backed by Intel, is one of the leading Chinese groups focused on developing AI chips for self-driving vehicles, surveillance cameras and other internet-connected smart devices. Horizon, which was co-founded by Yu Kai, who led the self-driving project at Baidu, has a partnership with Audi to develop self-driving cars in the eastern city of Wuxi (无锡). Another of Horizon’s chips runs facial recognition algorithms and enables cameras to identify faces from a database in the device of up to 50,000 faces. The fundraising is one of the biggest in China’s nascent AI chip sector and comes as the nation is aggressively building up its semiconductor industry.
 |
 |
Financial in China
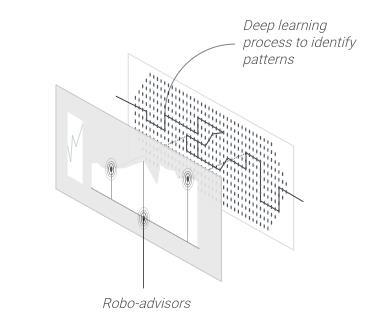
China’s national banks are testing AI applications for wealth management and fraud prevention. China’s robot-advisory market – platforms that provide automated, algorithm-driven financial planning – is expected to be the world’s largest by 2020. Globally, the segment is expected to expand to the US $6.5 trillion by 2025, up from the US $100 billion in 2016. Alan Qi, the chief data scientist at Alibaba Group mobile payments affiliate Ant Financial, said his company relies on artificial intelligence to improve customer service, assess the creditworthiness of applicants for its micro-loans, and calculate risks of issuing its insurance products. Artificial intelligence, he noted, enables Ant to serve the 900 million customers with fewer than 10,000 employees.
 |
 |
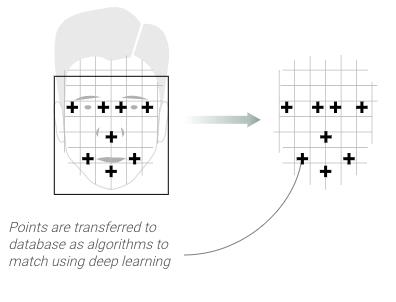
Facial-recognition in China
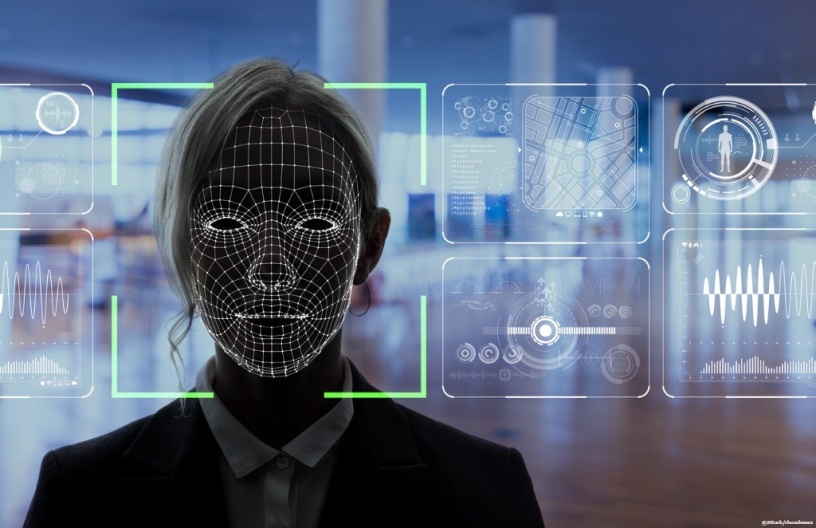
China is developing a facial recognition system with a database of 1.3 billion ID photos that can be matched in seconds, with an accuracy rate of 90 percent. Recently, SenseTime became the most valuable AI start-up in the world. The company drives China’s ambition to dominate global AI.
 |
 |
Retail in China
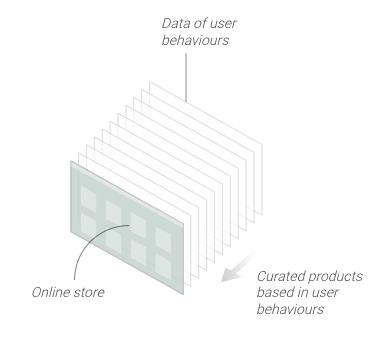
In 2017, 42 percent of global e-commerce transactions took place in China, more than France, Germany, Japan, Britain, and the United States combined. Big retailers have embraced online stores and chat-bot technologies, which can recommend products and predict when users will need certain products based on their online history and behavior. Alibaba drove the US $30 billion of sales over 24 hours on Singles’ Day in 2018, due to a combination of factors including consumer analytics using AI, machine learning, and cloud computing.
Robots in China

The Chinese robot market is forecast to grow at an average annual rate of 23.4 percent in the four years to 2019, much faster than global shipment growth of 13 percent, according to the International Federation of Robotics. China’s robot makers aim to supply 50 percent of the domestic market by 2020, rising to 70 percent by 2025. One of the most immediate and already live applications for robotics and artificial intelligence, in general, has been in using unmanned robots in warehouses and other environments, where they replace humans in repetitive jobs such as sorting and moving objects from A to B. In recent news, Beijing-based robotics startup Geek Plus (aka Geek+) says that it has raised $150 million dollars to seize that growing opportunity.
To date, Geek Plus says that it has delivered more than 5,000 robots across some 100 robotics warehouse projects in China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Japan, Australia, Singapore, Europe, and the United States. Current customers include Alibaba’s Tmall and VIP.com out of Asia. Thus, we see that technology is revolutionizing the supply chain, and Geek+ is one of the leading technology companies that are able to combine robotics, big data, AI and other cutting-edge technologies to solve the pain points of the traditional supply chain. As it accumulates more data and continues to optimize algorithms and expand into other industries, companies like Geek+ will continue to lead the revolution and innovation in the space within the Chinese market.
Embracing Growth in China’s AI industry
It is widely evident that the nation’s political and business leaders are betting that AI can jump-start the Chinese economy, especially during these times of geopolitical uncertainty and macroeconomic instability. However, as we are witnessing a slowdown in manufacturing growth, the country is now looking towards a future built around advanced technologies. Applying artificial intelligence may be the next step in this technologically-fueled economic miracle. While many in the West worry about AI eliminating jobs and worsening wealth and income inequality, China at the current moment seems to believe it can bring out positive outcomes and improve the world. Thus, transforming from a manufacturing powerhouse into an innovation-oriented digital economy will take a deep understanding of technology trends and thorough preparation in terms of capital, human talent and infrastructure.
Author: Jeffrey Craig
Eyetracking in China is one of the technological methodologies developed by Daxue Consulting.
The purpose of such methodology is to track and understand the behavior of Chinese consumers in specific situations. Through eye-tracking in China, our teams analyze the patterns of your target consumers according to different displays or stimuli.















