The Diabetes Treatment market in China
Urgent actions required to treat the explosive rate of diabetes in China
The diabetes treatment market in China is about to experience a boom, and this piece will explain why. For some background, Diabetes is a disorder of metabolism that impairs one’s ability to process blood glucose or blood sugar. The pancreas releases insulin to help body store and use the sugar and fat from the food eaten. Diabetes occurs when pancreas produces little or no insulin or when body does not respond appropriately to insulin. There are two most prevalent types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) and Type 2 diabetes (T2D). As there is currently no cure for diabetes, patients are required to actively manage their conditions to slow down the progression of such disease and stay healthy.
Type 1 diabetes in China (T1D):
Type 1 diabetes refers to the situation of deficient insulin production by the pancreas. Insulin is a type of hormone that allows sugar to enter cells to produce energy. The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes in China is unknown. Different factors, such as genetics and some viruses may contribute to type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes usually appears at a younger age. However, it can also develop in adults. It is more common among boys than girls in China and accounts for less than approximately 5% of the total diabetes incidences in China.
Type 2 diabetes in China (T2D):
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It’s characterized by body’s ineffective use of insulin. 90% of the diabetes patients around the world are diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. In most cases, it is the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity. The incidence of type 2 diabetes in China has been rising rapidly over the past few decades.
Diabetes in China: A public health crisis that should not be overlooked
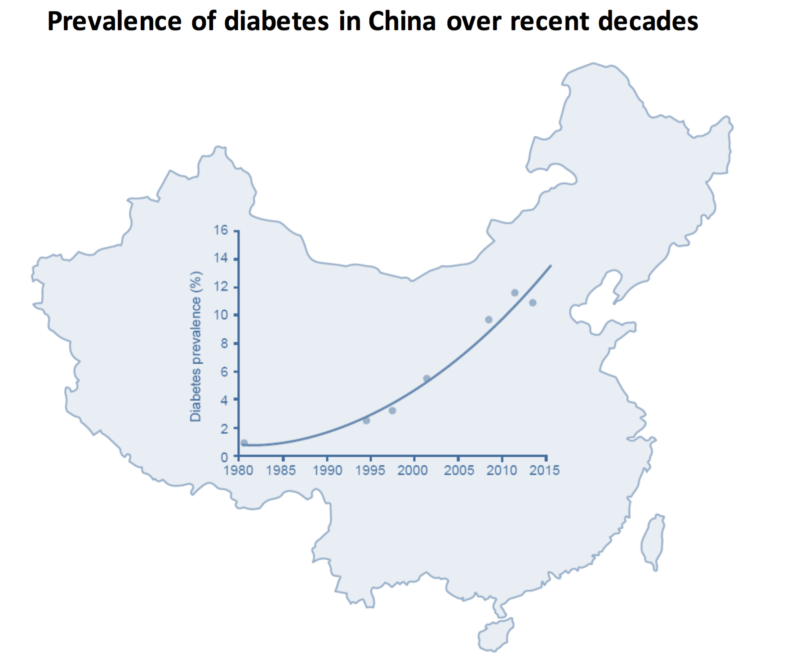
China is currently the country with the largest number of diabetes patients, which is around 109.6 million adults. The total Chinese population effected by diabetes is around 11%, not to mention a significant proportion remained undiagnosed. 415 million adults suffer from diabetes globally according to the latest finding of International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. This means China accounts for around 26% or over one-fifth of the total number of diabetes incidences globally. The prevalence of diabetes in China has increased drastically over the past few decades from less than 1% in 1980 to over 10% in 2013. The number is expected to continue grow to 150 million by 2040 if lack of action is taken to treat diabetes in China. Such high diabetes occurrence will result in many major social, health and economic consequences.
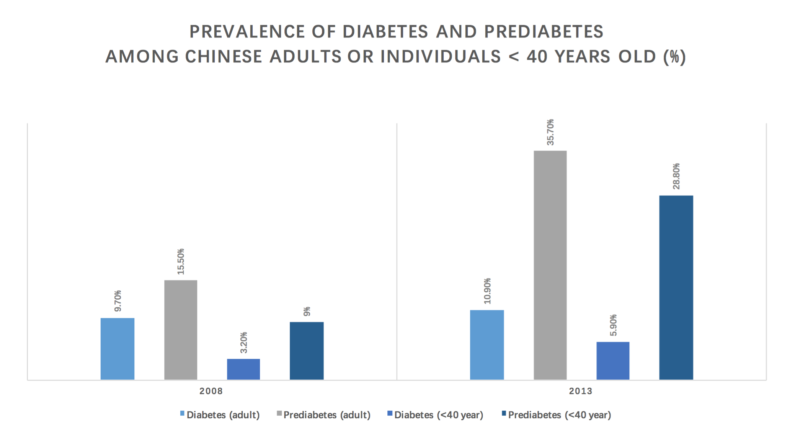
Prediabetes in China: affecting half of the population
Prediabetes is characterized by impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance. The estimated prevalence of prediabetes in China doubled from 15.5% in a 2008 survey to 35.7% in a 2013 survey. Almost half of all adults in China, around 500 million, have prediabetes in 2016. Although prediabets was more prevalent among senior population, especially men and overweight individuals, the prevalence of diabetes among younger generation was also relatively high and increasing.
While the prevalence of diabetes increased by 2.7% from 2008 to 2013 for the 20 to 39-year age group, the prevalence of prediabetes of the same population group had also increased from 9% in 2008 to 28.8 % in 2013. Moreover, across major ethnic groups in China, the prevalence of diabetes in the Manchu group was equal to that in the Chinese Han group, and the prevalence of prediabetes was even higher. The prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes is the lowest among Tibetan. Note not all minority ethnic group in China is included and Chinese Han is the majority ethnic group in China.
[Epidemiology and Genetic Risk Factors and Their Clinical Utility in Personalized Medication Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes in China]
[Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetic complications in China Prevalence of diabetes in China over recent decades]
Type two diabetes in China: Rising with obesity
It is estimated that Type 2 accounts for more than 95% of all diabetes cases in China. The dramatic increase in diabetes prevalence is also largely attributable to Type 2 diabetes. The rapid increase of Type 2 diabetes should be considered in accordance with the increase of over-weight and obesity cases in China that may be driven by economic development as well as lifestyle and diet change.
Although Type 1 diabetes is not as common in China, the prevalence of such type of diabetes has been gradually increasing over the past decades. Notably, type 1 diabetes among Chinese children below 15 years has been increasing by 4.4% each year between 1995 and 2010. Although, the explosive prevalence rates of both Type 1 diabetes in China and Type 2 Diabetes in China suggest that urgent actions should be taken, many factors still post challenges on the effectiveness of Chinese diabetes treatment market.
Challenges to effectively treat diabetes in China
The fact that 63.5% of diabetes in China still remain undiagnosed and that over 60 million patients have not yet received any diabetes treatments suggest in many ways that the diagnose and treatment of such disease faces great challenge.
Challenge in the diagnosis of T2D in China
The probability of diagnosing diabetes decreases as both fasting plasma glucose and oral glucose tolerance tests require the patients to fast for at least 8 hours. Moreover, no Chinese-specific diagnostic value for HbA1c has been established. In general, HbA1c cutoff points vary according to ethnic groups, age, sex and the prevalence of diabetes. The wide use of HbA1c as a diagnostic tool has been limited as significant difference in availability and standardization of HbA1c assay methods exist across Chinese laboratories. Not to mention that T1D in China is also fairly difficult to be accurately diagnosed due the variation in access to and delivery of care for T1D patients.
Increasing obesity and overweight population
The rapid increase in the prevalence of T2D in China can not be considered without its linkage with obesity and overweight. The prevalence of overweight increased from 37.4% in 2000 to 41.2% in 2014 among Chinese adults aged 20-59 years. The estimate increase is 0.27% per year. On the other hand, the prevalence of obesity, with an estimate increase of 0.32% per year, had increased from 8.6% in 2000 to 12.9% in 2014 for the same Chinese age group. The continuous and rapid expansion of overweight and obesity population will likely put more pressure and burden on the prevention and treatment of diabetes as both are direct causes of T2D diabetes.
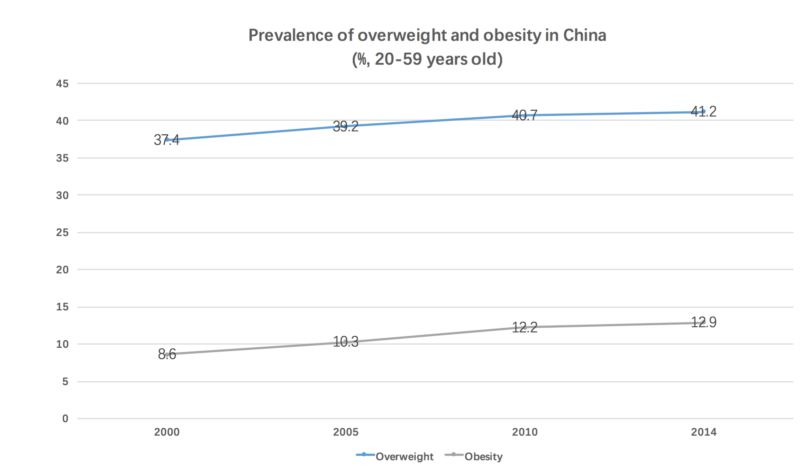
[Source: Diabetes in China: Epidemiology and Genetic Risk Factors and Their Clinical Utility in Personalized Medication Prevalence of overweight and obesity in China]
China’s population develops diabetes at a much lower BMI compared to westerners
One big challenge of the Chinese diabetes treatment market is attributable to the finding that Chinese people are more likely to develop T2D at a considerably lower BMI compared to Western populations. BMI, or in another word Body Mass Index, is a measure of healthy weight using one’s height and weight.
A healthy BMI for most adults is between 18.5 and 24.9. However, according to a recent national survey, diabetes and prevalence of diabetes for participants with an ideal BMI less than 23 kg/m2 was 6.4% and 30.7%. The mean BMI of T2D diabetes patients in China are around 25 kg/m2. Both suggest that BMI and adiposity relationship differs between different populations. The relatively higher risk of T2D at a lower BMI for the Chinese population may be partly explained by Asians having a higher percentage of body fat than those of Europeans at the same BMI and by the tendency toward visceral adiposity in East Asian population which includes Chinese people.
In addition, East Asian population, when compared to European or African populations, have also been found to have a higher insulin sensitivity with a much lower insulin response. This suggests a -cell dysfunction, which has been proven a major determinant of T2D diabetes in China. Furthermore, diabetic nephropathy was also more common among Chinese population than Europeans. Therefore, more specific and urgent strategies are required to prevent and diagnose diabetes and associated diabetic complications as Chinese population are exposed to a much higher risk.
The increasing prevalence of early-onset diabetes in China
The increase of early-onset diabetes in China should not be overlooked. Now, approximately 20% of diabetes patients in China are diagnosed before the age of 40. Individuals suffering from diabetes from a young age will have a higher risk of chronic complications, which will lead to mortality and morbidity in diabetes. Young-onset diabetes patients often had worse glycaemic control and higher prevalence of retinopathy. They were also less likely to be effectively treated with HbA1c and LDL, and to receive organ-protective drugs, such as statins and renin–angiotensin system inhibitors than late-onset diabetes. Moreover, Chinese early-onset diabetes patients had a higher risk of nonfatal cardiovascular disease. This tendency of early-onset diabetes in China should be alarming as it is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Chinese diabetes treatment market: An overview of the diabetes treatment products in China
A significant gap still remains in the Chinese diabetes treatment market as only 5.6% of diabetes patients are achieving optimal control of blood glycose, blood pressure and lipid targets concurrently. Optimal diabetes control requires good medical care, patient empowerment, health literacy and self-discipline.
Non-Insulin medicines used in Type 2 diabetes treatment market in China
First-line oral anti-diabetes agents in China
Metformin
Metformin is used along with other medications to control high blood sugar or down regulate gluconegenesis in the liver. As metformin does not increase weight, it is often the first choice of medication for T2D. However, metformin cannot be used if the patients have kidney or liver problems, heart failure or is very sick. Low blood sugar may be seen if metformin is taken with insulin on Secretagogues.
[Source: 302hospital.com Metformin pills available in the Chinese market]
Secondary oral antidiabetes agents in China
Secondary oral medications, such as sulfonylureas, glinides, thiazolidinediones and DPP-4 insulin are normally taken if metformin monotherapy fails to work.
Secretagogue
Due to the postprandial hyperglycemia in Chinese patients, insulin secretagogue or -glucosidase inhibitor is recommended over metformin for patients who would experience diarrhea or stomach cramping as side effect of metformin. Secretagogue or insulin releasing pills include sulfonylureas and glinides. The most common types of sulfonylureas are glyburide, glipizide and glimepiride. Sulfonylureas lowers blood sugar by releasing insulin through beta cell stimulating. However, it only works if pancreas has beta cells. Glinide works the same as sulfonylureas. However, it’s effectiveness duration is not as long as sulfonylureas and must be taken up to 30 mins before each meal. The side effects of secretagogues are low blood sugar and weight gain, and again may not be used if the patient has live or kidney problem.
Thiazolidinediones
Thiazolidinediones lowers blood sugar by increasing the sensitivity to insulin of muscle, fat and liver. It is also known as the insulin sensitizer as it can normalize blood sugar level without the risk of low blood sugar. This type of drug usually takes a several weeks before it can start working. The side effects include weight gain, fluid retention, and anemia. Moreover, women taking thiazolidinediones have a greater chance of bone fracture as it increases fat particles (LDL).
DPP-4 Inhibitors
T2D patients usually suffer from high blood sugar due to glucagon levels after meals. Incretin based treatments such as DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 analogs in China are used as post-meal glucagon to reduce post meal blood sugar level. Both medicines are blood sugar normalizing medications and euglycemics. Sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin are all pill types of DPP-4 inhibitors. They can block DPP-4 enzyme from breaking down GLP-1 quickly. DPP-4 inhibitors are normally used along with other diabetes medicines to control sugar level further.
GLP-1 Analogs
Exenatide and liraglutide are injection types of GLP-1 analogs in China to regulate blood sugar levels from rising after fasting. GLP-1 analogs are incretin hormones and act like natural hormone. They are released in the gut when eating and quickly broken down in the bloodstream by DPP-4. It is developed to resist breakdown by the enzyme DPP-4. However, it will create a feeling of satiety.
Insulin and Insulin Analogs used in Type 2 diabetes treatment market in China
Insulin is often categorized by the differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration and route of delivery. It is usually injected into fatty tissue right under the skin. Human insulin and insulin analogs are used for replacement therapy. Regular human insulin usually has an onset of 0.5-1 hour, peak effect of 4 hours and a duration of action of 6-8 hours. Generally, the larger the dosage, the faster the onset of action and longer peak and duration effect. NPH human insulin and pre-mixed other types of human insulin.
Insulin analogs in China have been developed as human insulin in China retains many limitations when injected into the skin. Human insulin clumps together with high concentration, which will cause slow and unpredictable absorption from subcutaneous tissue and a prolonged action duration. However, the action duration of insulin analogs in China can be predicted and it works quicker with an even effect. Insulin analogs includes rapid acting insulin analogs and long acting insulin analogs.
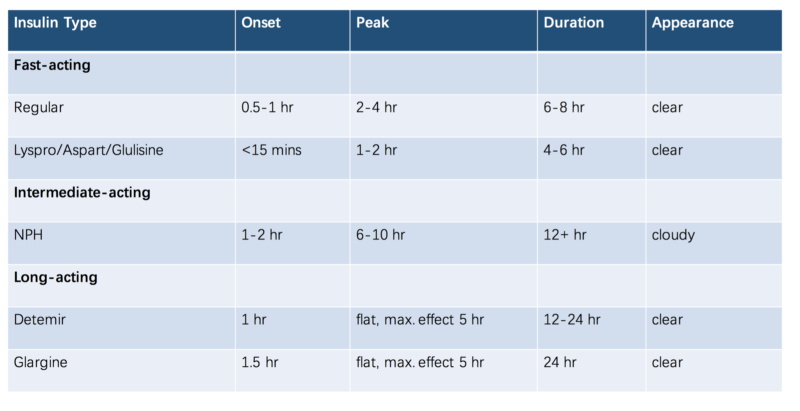
[Source: Diabetes Teaching Centre at UCSF Insulin properties]
Type 1 diabetes treatment market in China
As T1D does not produce enough insulin, it has to be replaced. Therefore, insulin therapy and non-insulin treatments such as amylin analogs and insulin pump therapy is used. Insulin therapy is normally prescribed by doctors and is an injection type of diabetes treatment in China. Intensive insulin may sometimes by used to mimic the body’s normal pattern of insulin secretion and it will require multiple daily injection of insulin or insulin pump therapy.
Pramlintide in China
Pramlintide in China is an injection type of diabetes medicine for both T1D and T2D patients to control blood sugar levels after eating. It resembles amylin, which is the hormone that is released with insulin from the pancreas beta cells. It is a more common type of treatment for T1D as amylin levels are absents due to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction for T1D.
Insulin pump therapy in China
Insulin pump therapy is becoming increasingly popular as a method of insulin replacement therapy in China. As it mimics what body does naturally, it can improve blood sugar control of patients more effectively. T2D in China also uses such method.
Overall, insulin products account for 42.5% of all diabetes medicines available in the Chinese market and traditional oral diabetic medicines account for 51.1%. 3rd generation insulin occupies 34.4% of the insulin products market and 2nd generation insulin products are becoming more mature and stable in its price. New blood glucose regulating medicines such as DPP-4, GLP-1 and SGLT-2 occupy less than 7% of the market share each. However, they are considered the main medicines that will expend the diabetes treatment market in China.
The Chinese diabetes treatment market lags behind other countries as traditional oral diabetic medicines are still the main forms. In 2017, 5 types of DPP-4 inhibitors were included in medical care, and 3 new types of SGLT-2 inhibitors entered the Chinese market. It was expected that these new forms of diabetic treatment drugs will expend in market size as more generic drugs become available in the market that will lower the cost.
Monitoring devices available in the Chinese diabetes treatment market
In order to maintain a normal blood sugar level and prevent tissue damage caused by high blood sugar among diabetes patients, many devices are used to achieve such goals. The normal blood sugar level is around 60 – 100 mg/dl overnight and before meals, as well as < 140 mg/dl after meals.
Blood Monitoring
Blood glucose should be checked throughout different times of the day. The good times to check are after meals or whenever nor feeling the best. People that takes medications to insulin secretion from pancreas will need to check more often.
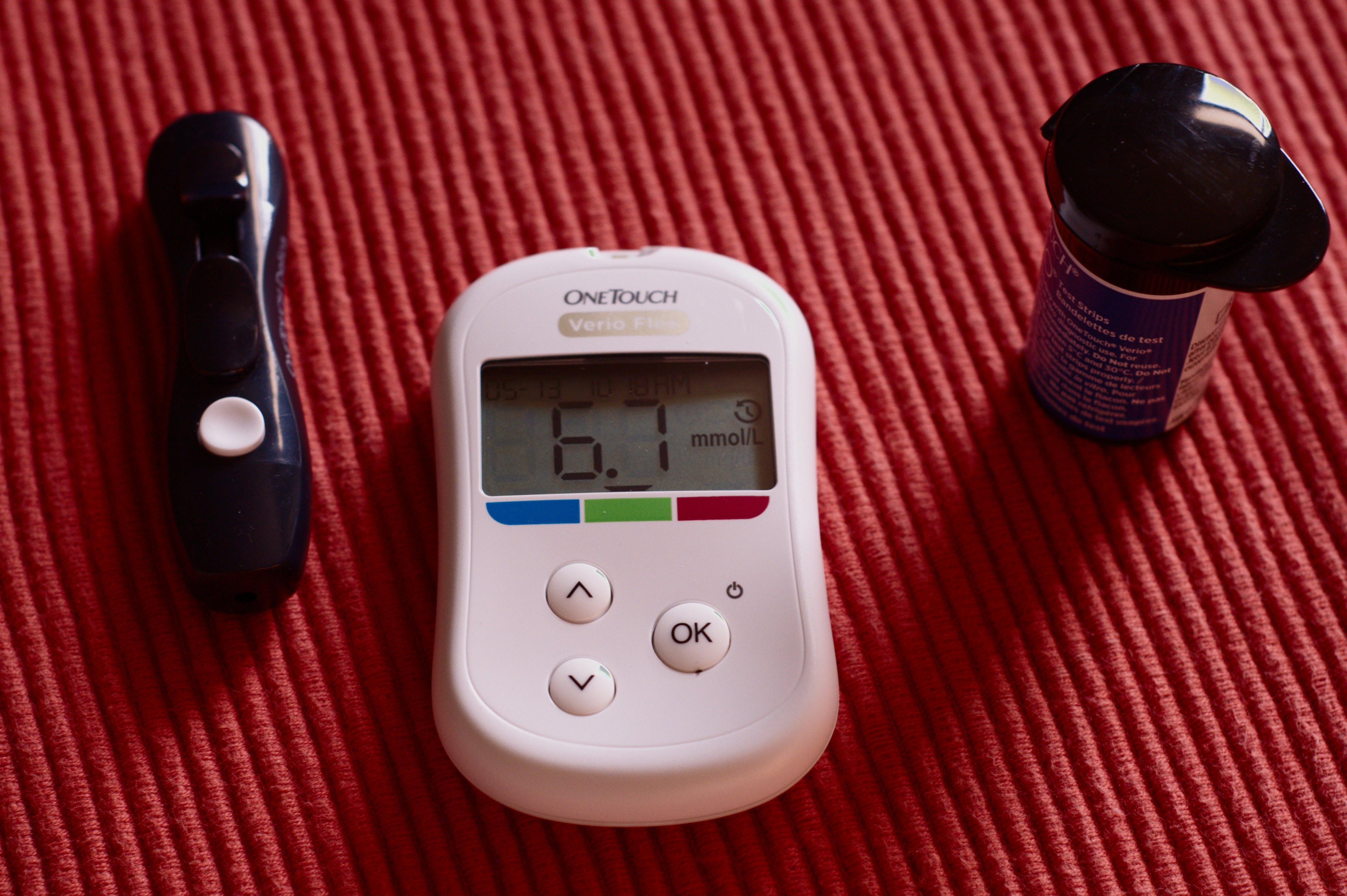
Glucose meters
Using a drop of blood, glucose can effectively measure the blood sugar level of an individual. There are fingerstick testing glucose meters and alternative site testing glucose meters. There are various brands and models for fingerstick testing glucose meters and it is a more common types of device. Both meters only provide a similar result if one’s blood sugar is stable. Fingerstick testing is till the most accurate type of meter. Glucose meters are readily accessible in the Chinese market. Diabetes patients can purchase the devices through various online and offline channels. However, multiple brands sale such devices at various costs, which makes it difficult for patients to choose the rightful one.
[Source: zhizhizhi.com Glucose meter]
Continuous glucose monitors (CGM)
Continuous glucose monitor measure glucose in body fluids between cells. It does not measure blood glucose level directly. It is usually changed every few days to weeks. Sensors are taped to the skin and will continuously collect glucose reading. This device adopts an alarm function for high and low blood sugar level and trend alarm for early intervention. It also allows 24-hour trend data and improves blood glucose control more effectively.
Domestic and foreign brands in the Chinese diabetes treatment market
Foreign brands still dominate the diabetes treatment market in China. They remain as the major contributors of new diabetic drug innovations. Although some domestic brands are among the top players in the market, their presence are normally stronger in the generic drugs field. Generally, foreign brands compete upon new innovation and new product development, while domestic brands compete upon cost leadership。
Novo Nordisk®’s Ozempic® (semaglutide) injection for T2D patients
Ozempic® is an injection type of GLP-1 receptor agonist. Novo Nordisk ® had submitted 5 clinical applications for Ozempic according to CDE as at end of 2019 with an intention to launch this product as soon as possible in the Chinese diabetes treatment market. The successful launch of Ozempic in China by Novo Nordisk will accelerate the research process and increase the availability of semaglutide in the Chinese market. The market for GLP-1 receptor agonist continues to expend as it carries great blood glucose regulation ability and protects beta cell at no risk of weight gain or hypoglycemia. The global market size of GLP-1 receptor was around 8.827 billion usd with a compound annual growth rate of 35.7% in 2018, which was far higher than overall growth rate of diabetes medicines market. Therefore, GLP-1 will definitely become the core contributor to the future growth and expansion of the Chinese diabetes treatment market. Although the advantage of Liraglutide will continue to be seen as it is the only GLP-1 Ra product included in the National medical care, Semaglutide will gradually replace Liraglutide in the long term. As both Semaglutide and Liraglutide are produced by Novo Nordisk, its major position within the Chinese diabetes treatment market will continue to be supported.

[Source: Yaofangwang.com Victoza® produced by Novo Nordisk®]
The total sales generated in the Chinese market for Q3 2019 by Novo Nordisk was around 10.14 billion rmb. Its Chinese market sales accounted for around 10.96% of its total global sales with a growth rate reaching 15%. Diabetic medicines and injections produced by Novo Nordisk currently occupies more than 27% of the total diabetes treatment market in China. Notably, liraglutide injection Victoza® produced by Novo Nordisk accounts for more than 92% of the total GLP-1 Ra market in China. Moreover, Novo Nordisk had successfully launched san evolutional pill type semaglutide Rybelsus® in the U.S, which is expected to enter the Chinese market in the near future.
Yabao Pharmaceutical launching the generic drug “Alogliptin benzoate tablets”
Yabao pharmaceutical is a domestic research and development based company for innovative and generic drugs, traditional Chinese medicine and big health products. By launching such type of generic drug, the firm will adopt a more competitiveness position and a more profitable prospect. Generic drugs can usually reduce health care costs for and increase the availability of medicines to the general public. Alogliptin is one type of DPP-4 inhibitor that was first invented and produced by a Japanese firm named Takeda pharmaceutical. The original drug was named Nesina® and was designed especially for T2D patients. Alogliptin benzoate contains active ingredient alogliptin that can slow the inactivation of incretin hormones, and hence can increase blood stream concentrations well as reduce glucose concentrations post meal for T2D patients. It encourages beta cells to release insulin, while inhibits glucagon released by alpha cells.
[Source: jd.com Nesina® Alogliptin benzoate tablets produced by foreign firm Takeda pharmaceutical]
There are currently 3 types of domestically produced DPP-4 inhibitors. The first two types of DPP-4 inhibitors launched were Shagliptin and Vigliptin by Aosaikang Pharm, Hansoh pharma and Qilu Pharmaceutical. Yabao will become the first to launch a generic drug for alogliptin and the third to launch a domestic DPP-4 inhibitor in the Chinese diabetes treatment market if it is successfully launched into the market. Although insulin is still the main product used for diabetes treatment, new forms of medicines such as DPP-4, GLP-1 and SGLT-2 are becoming more popular. DPP-4 inhibitors occupy around 25.5% market share. Despite GLP-1 is experiencing high growth, the importance and popularity of DPP-4 will not be easily shaken.
Opportunities in the diabetes treatment market in China
In 2017, the market size of diabetes treatment market in China was 5.76 billion rmb with annual growth rate of 3.69%. China’s health care costs associated with diabetes were around 200 billion rmb in 2007, and is expected to exceed 360 billion rmb by 2030. The large number of people affected by diabetes, the large proportion of undiagnosed diabetes, and ineffective control of risk factors of diabetes patients who are actively taking treatment suggests the burden on the healthcare system in China both at present and in the near future.
The current management of T2D in China is not optimist, despite various treatment patterns for diabetes are present. According to the survey of China noncommunicable chronic diseases, diabetes treatment for urban residents was 41.8% and for rural residents was 27.6%. Optimal glycemic control was only achieved by half of treated patients. China currently encourages the “3B study”, which aims to investigating blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lipid control among T2D patients in China. The amount of patients who have achieved individual target goals are 47.7%, 28.8% and 36.1% respectively. However, only 5.6% of all patients have successfully managed all three target goals.
Increase education on diabetes prevention and treatment
Diabetes treatment not only requires active medical care, but also self-discipline and self-management by patients. Therefore, information on diabetes should be more readily accessible and educations upon the prevention and treatment of diabetes should be valued. This creates market opportunity in nursing and health education in China.
Information technology that improves the management of blood glucose levels among diabetes patients
A symptom that greatly increases the risk of T2D is metabolic syndrome. More innovative methods are required to improve the management of cardiovascular risks associated with prediabetes or diabetes patients. Many health information technologies (HIT) have been developed and proofed to be effective tool to control blood pressure and blood glucose levels among diabetes patients. Generally, the role of HIT is to manage diabetes via supporting provider decision-making through electronic risk assessment, guidelines and prescribing etc. Patients can also self-manage through risk communication, web portals and telemedicine etc. HIT exerts significant effect on glycemic control and on risk factor monitoring and measurement. Therefore, HIT is useful to achieve more optimal diabetes care. However, future studies are required to investigate more in depth, the adoptability and feasibility of different types of HITs to each risk factors.
Noninvasive diabetes monitoring devices
Glucose monitoring devices are becoming much more popular along with the prevalence of diabetes. However, most monitoring devices that are available in the diabetes treatment market in China requires invasive blood glucose monitoring. However, new forms of blood glucose monitoring devices requires no finger sticks anymore. This means glucose levels can be tested pain-free, blood-free and needle-free, and most importantly unlimited and continuous testing are readily accessible whenever and wherever as user requires. Although such product is not receiving positive feedback currently as it has not yet received permit from CFDA, it will become a future trend nonetheless.
[Source: GlucoTrack® GlucoTrack invented the first noninvasive glucose monitoring device]
Market opportunity for foreign diabetes treatment companies
Overall, the diabetes treatment market in China is experiencing high growth due to the explosive rate of diabetes in China. However, more weight and attention should be placed on the Chinese diabetes market in order to effectively control the incremental rate of diabetes patients. By achieving such target, government support on health care system and new innovative methods to provide more convenient monitoring and diagnosing of diabetes patients will be required.
Due to the high demand for treatment and the government support, now is the right time to enter the market. Start your China market research project on diabetes in China by emailing dx@daxueconsulting.com
Let China Paradigm have a positive impact on your business!
Listen to China Paradigm on iTunes