China’s startup scene: Lively, relentless, and unmatched by anything else
China’s startup scene has its ups and downs but has never been inactive. The country has long recognized the importance of startups in boosting economy and employment, and therefore has invested in startup ecosystems. On the one hand, the huge and homogeneous Chinese market offers a natural experiment field for aspiring entrepreneurs. On the other hand, acquisition from tech giants, competition from copycats and illegal attacks are obstacles to growth. Just as there is no shortage of opportunities in China, there is no shortage of startups. For the true visionaries, the worst time is usually also the best time.
China’s startup hype started from the central government
Entrepreneurship and innovation have always been on the mind of top decision makers
Since 2008, China’s central government has already extended a warm welcome (in the form of grants and other perks) to attract top talents back to China. Its goal is to promote high-level innovations and technological breakthroughs, which naturally contributes to employment and economy.
In 2014 in the Summer Davos Forum, the Prime Minister Li Keqiang first coined the term “Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation”. In 2015, he kept advocating the entrepreneur spirit in the National People’s Congress and many other important occasions. Since then, the notion of starting up and being your own boss gained momentum.
Over the years, the Chinese government has focused on the youth as the main propeller of innovation
The plan called “Implementing Opinions on Deepening Innovation and Entrepreneurship Education Reform in Higher Education Institutions” issued by the State Council in 2015 further lowered the entry barriers for university graduates to start a business. All sorts of business plan competitions were put in place with generous grants to realize the winning proposals. For example, China College students’ Internet Plus Competitions are target local graduate students, while the Chunhui Cup targets overseas students. Also, startup experiences could be converted into school credits. What’s more, university entrepreneurs can extend their school years if they decide to pursue a business idea.
All those measures were established to reach the objective in 2020: a sound university entrepreneurship education system, significantly enhanced students’ innovative spirit and skills, and a significant increase in the number of students engaged in entrepreneurial practices.
Internet is transforming almost all the industries, representing great opportunity for mass innovation
The term “Internet Plus” was coined to inspire people with the prowess of information technology, and is regarded as a national-level strategy. All the aspiring entrepreneurs in China’s startup scene are thinking how to disrupt a traditional industry with the mighty internet.
Online to Offline (O2O) is a famous term born in this context. The logic is to combine the online and offline experience to facilitate life. Ride-hailing market leader Didi, food delivery platform Eleme, e-commerce giant Taobao, short-lived bike-sharing unicorn OFO are all examples of the O2O business model. The customer value chain has one part done online, usually product configuration and mobile payment, and another part delivered offline.
In addition to O2O business model, Internet Plus also gave birth to new business models in various industries. Coupled with media, it became new media, embodied by WeChat official accounts. Married with finance, it turned into FinTech, which made investing, money wiring, and short-term renting way more convenient. E-commerce is the best illustration of how internet switched the retail business online and scaled up its influence while cutting down fixed costs.
The benefit of internet spills over to non-for-profit areas too. For example, online education market leader Hujiang put forward a Corporate Social Responsibility program in 2015, with an aim to mitigate the education inequality in China. Ant Forest, a carbon-reduction program introduced by Alipay increased user stickiness by planting real trees on their behalf.
The mobilized public and the honorable badge of failure
The unwavering support from the government and the widespread of internet capabilities enabled the creative minds to unleash their potential.
According to National Bureau of Statistics, the improvement of general business environment in China has given rise to business registrations. Especially in the tertiary sector, where the legal entities registered with IT services has quadrupled from 2013 to 2018. Other booming industries include technological services, leasing and professional services, with a CAGR of 23%. Public administration and social organizations only grew 2% on an annual basis. Those figures clearly outline the confidence and concentration of digital services promoted in the entrepreneurial wave.
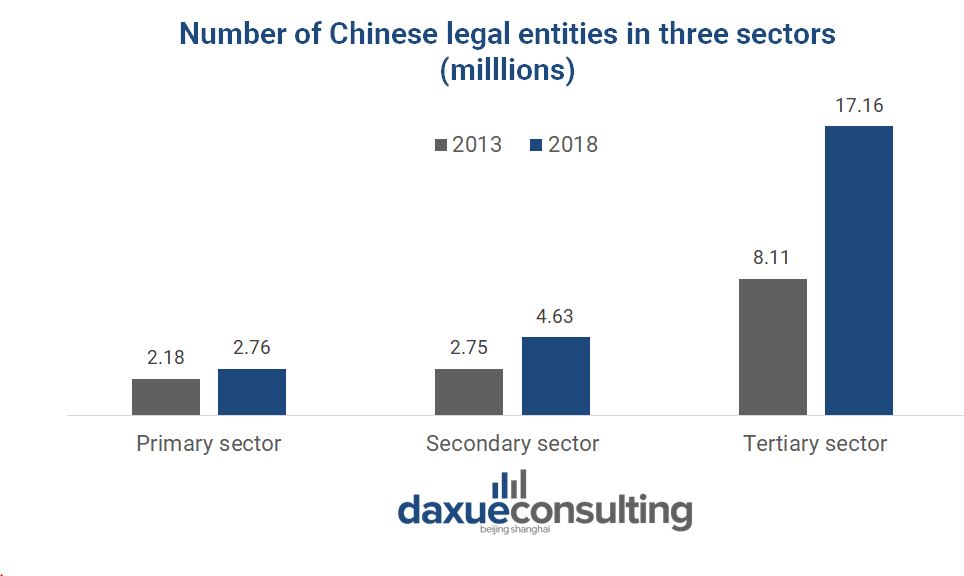
Data source: National Bureau of Statistics, Number of Chinese legal entities in 3 sectors
The increased ease of starting up and technological advancements propelled the establishment of enterprises. Compared to individual economic units, registered enterprises soared in 5 years, taking a whopping 75.6% of total legal entities.
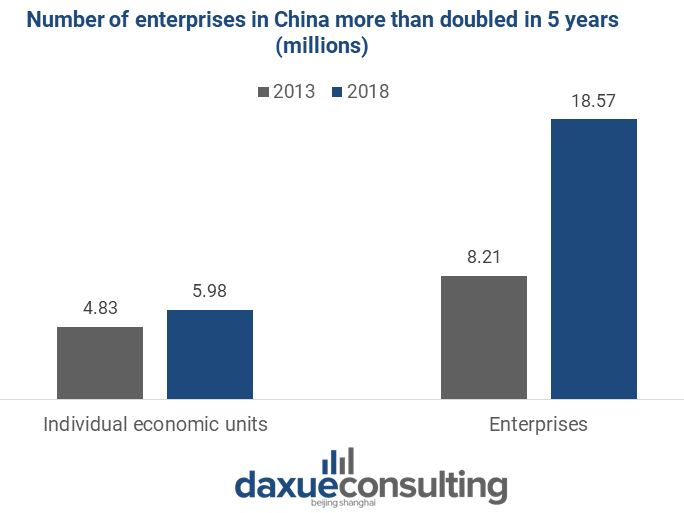
Data source: National Bureau of Statistics, Number of Chinese enterprises registered has soared
Furthermore, the tide of Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation translated into the numerous young enterprises. In 2013, SME (small and medium enterprises) represented 95.6% of the total registered companies. In 2018, they represented 98.5%, showing the liveliness of Chinese entrepreneurial energies.
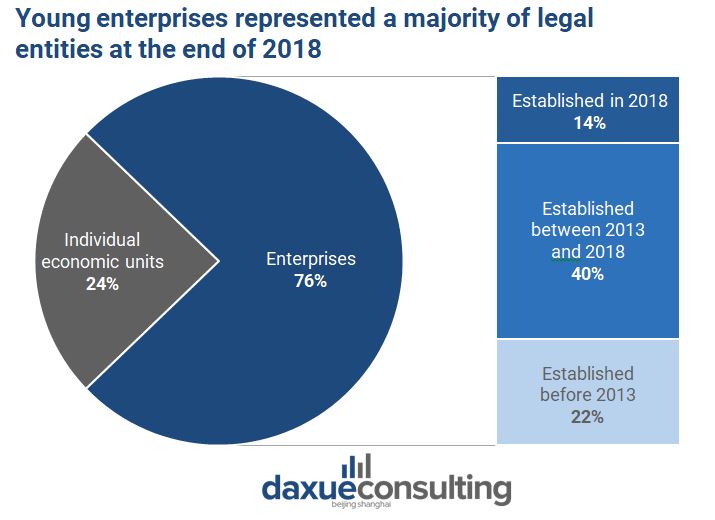
Data source: National Bureau of Statistics, Young enterprises take the lead
There are many stories and lessons about startup failures, which is how 95% of startups end. But with the mainstream endorsement and regulatory privileges, failures are more and more seen as a badge of honor. For the new generation of Chinese entrepreneurs, many are driven by dreams and opportunities, some are forced to venture for lack of job prospects, yet others are blindly following suit. In 2011, only 1.7% of university graduates opted for starting up a business. This percentage peaked at 3% in 2016 then slightly dropped to 2.7% in 2018. This change implies that government promotion was effective, and that China’s startup scene is cooler headed than before.
On the one hand, it’s the government’s job to put all the necessary support in place to ensure new ideas come out alive after market selection. There are more and more incubators, governmental subsidies, and free startup resources and mentors. On the other hand, it’s entrepreneurs’ job to hone their entrepreneurial skills and think long and hard about their fundamental business logic.
The fallen unicorns made investors more cautious about the fundamental business logic
After the two roles played by the government and the entrepreneurs, the third player in China’s startup scene is the investors. Whether it’s business angels or venture capitalists or private equity firms, they are the guardians of solid business sense and financial resources.
The loudest failure in the recent history of China’s startup scene is the bike-sharing platforms. Began in 2014, OFO and Mobike had been the super stars to solve the last mile mobility issue. Even with around 8 billion RMB of investment across several rounds for each company, they had been controversial in their ability to generate profit, to respect public order, and to protect local environment. In the end, OFO filed for bankruptcy and Mobile got acquired by Meituan for merely 2.7 billion RMB.
This contrast of capital zeal and the market failure illustrate the short-term mindset of some investors. To claim the maximum market coverage, which seemed to be the key success factor in the sharing economy logic, the companies and the capital both prioritized buying bikes over risk control. The lack of a sustainable company culture and conflicts of interest at the top management level went unaddressed.
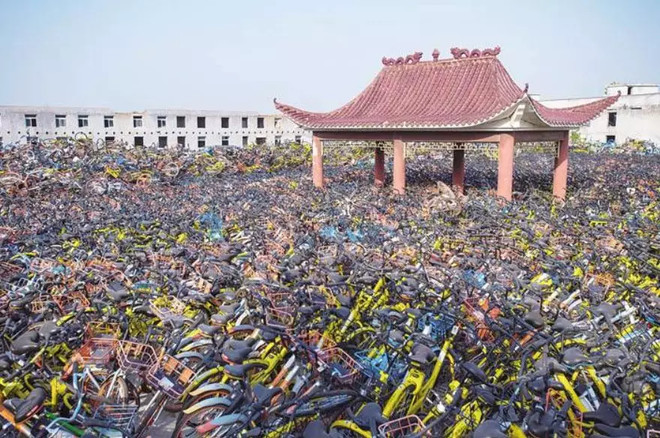

Source: Sina Finance, the mountain of abandoned sharing bikes
Such a vivid example will lead the investors to favor sound business models over those benefiting from over-evaluations of other investors. It’s good for the society because it creates less bubbles, but it also means tougher financing for the entrepreneurs. For any newcomer in China’s startup scene, there are several dangers that could be detrimental to its fundamental business logic.
Competition and acquisition from conglomerates like BATJ
It’s almost a common knowledge that once a startup is big enough, it will be bought by one of the tech giants in China. The famous Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, JD and other rising giants like ByteDance, NetEase, Didi, Meituan won’t hesitate to make a bid to make their own ecosystems stronger.
But first of all, the startup has to survive the competition by those giants. A great dark-horse example is Pinduoduo, whose founder Colin Huang recently became the second richest person in China. The notion of Social + Ecommerce in the long tail market made this startup successful, in an era where everyone thought Alibaba and JD had occupied all the room of growth. In theory, the existing e-commerce giants could quickly take over Pinduoduo in its cradle. In practice, neither of them followed the startup to compete in lower-tier cities.
Tencent, being the social networking giant, strategically invested in both JD and Pinduoduo, to combat with Alibaba in the e-commerce arena. That’s the best outcome for the startup, with the owner taking 46.8% of the shares and 89.8% of the voting rights.
Other startups don’t have the same luck, many were bought to be dissembled into existing projects of the giant company. For example, ByteDance bought Zhaoxi Calendar, a niche time-management app, whose product team was integrated into Lark, another acquisition realized only 2 month before.
Copycats and price war
Even if a startup didn’t make enemies out of the tech giants, diligent copycats and the resulting price war could put an end to their cash inflow.
The Chinese market never lack duets. Didi and Uber China in ride-railing sector, Meituan and Eleme in food delivery online business, Mobike and OFO in bike sharing economy. When there is oligopolistic competition, the consumers are the happiest. Huge amounts of discounts are up for the taking, as long as they lead to market share. However, price wars are destructive to both competitors, as the customers attracted by low price are not necessarily loyal. Once the price incentives are out of the table, usually due to the serious drain on financial resources, the market share might shrink back.
One sure thing to note about China’s startup scene is that, there is no shortage of copycats. Demonstrating this, there are more than 20 startups which share the same shared-bike business model.

Source: Tencent news, Shu Ke Shi, 20 startups in bike sharing industry
Illegal activities that suck the margin into the shadow
Luckin coffee has made its fame by publicly stating financial fraud to SEC. Its business model was clearly unsustainable, as it had a loophole in its expansion strategy. It’s strength in marketing and storytelling did not compensate its unsatisfactory risk control department. And this Achilles’ heel has costed its healthy financial performance.
Basically, Luckin’s expansion strategy is based on customer referral. As a startup, the number of referrals is directly linked with GMV, KPI, and valuation of next financing round. It’s therefore understandable how much marketing and budgetary resources are pooled to facilitate leads conversion. However, instead of using elaborative verification methods to ensure the referred customer is a real person, Luckin only used a phone number to validate the referral. Once the referral is validated, both the referrer and the referee enjoy discounts. The result of a weak risk control is constant loss of profit due to a highly developed grey industry of fake phone numbers.
In the highly competitive battlefield as the China’s startup scene, nothing is too despicable to be true. Entrepreneurs owe it to their teams and investors to pay attention to not only the legal competitions, but also illegal activities.
In conclusion, China’s entrepreneurs keep pushing forward despite setbacks
China’s startup scene is quite lively thanks to the government’s Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation guidelines, mobilized public and responsible investors. Even though system-level crises, industry-level fluctuations, and company-level setbacks keep striking one after another, the qualified entrepreneurs will seize the opportunity in the distressing time, fearless as always.
Author: Della Wang
Interested in starting a business in China?
Start with China Paradigm and learn about over 100 China entrepreneurship ventures
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast