The organic food market in China
The definition of organic food in China
The for organic production, including atmosphere quality, organic irrigation water, unpolluted soil and natural processing. Organic food in China has to satisfy the following requirements:
“Complying with specific principles of agricultural production, production did not use raw materials or products generated by genetic engineering, did not use chemical syntheses such as pesticides, fertilizers, growth regulators or feed additives. It also needs to follow natural rules and adopt a series of techniques to maintain sustainable agricultural production.”
Organic food production models in China: the system production is the main force
In China, most organic foods are cultivated by organized systems, not like other countries where organic foods are supplied by individuals. There are three mains organic food production models in China: the first one is that big company leases land from farmer and pays them. The second model is that under the permission of local governments, big companies sign an organic food production contract with farmers. The third one is the organic producer association. Farmers set up an association by themselves to conduct large-scale organic food production.
The categories of organic food in China
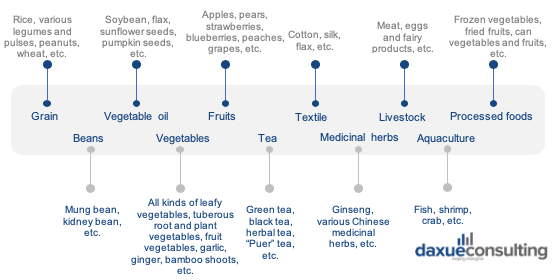
Due to vast cultivation areas and various climates, diverse organic food can be grown in China. The main organic products exported are processed vegetables, soybeans, honey, grains, green tea, herbal medicines and beans, which are mostly raw and semi-processed.
The development of the organic food industry in China
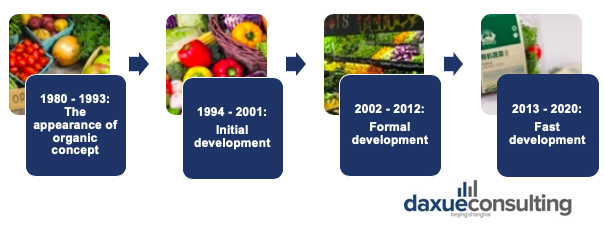
[Source: International Trade center. The development of the organic food industry in China]
The concept of organic food was introduced in China after the reform and opening-up policy. By 2018, China’s organic agriculture acreage ranked third in the world, accounting for 4.5% of the total acreage of global organic agriculture and 50% in Asia. From 2002 to 2013, many laws were introduced to regulate the orderly market environment of organic agriculture. Thus after 2013, organic agriculture in China entered a stage of rapid development.
The evolution of the organic food market in China.
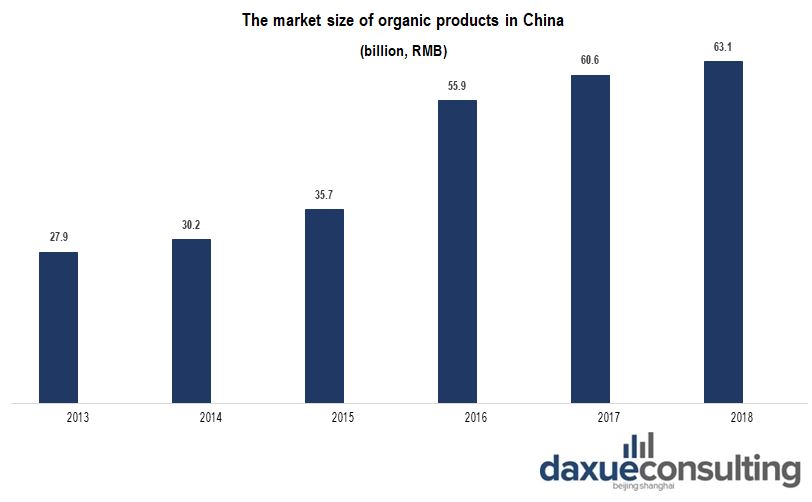
Looking at the evolution of the market, we can definitely say that organic food in China has huge potential in international and domestic markets. Just in 2018, domestic sales of organic products in China were about ¥63.15 billion, up 4.01% from ¥60.67 billion in 2017. Besides, e-commerce largely stimulated sales of organic food in China. At present, the market size of organic food in China is still very low, which is far from meeting the needs of domestic and foreign consumers.
Organic packaged foods and beverages lead organic food consumption
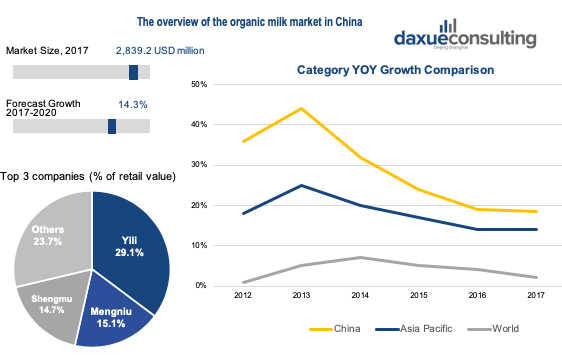
Unlike other countries which mainly consume organic vegetables and fruit, organic milk dominates China’s organic market because of its nutrition and perceived benefits to the immune system. Ranking as the 4th largest market in the world by value, China’s total market size for organic packaged food and beverages in 2017 was $2,839.2 million. As for China’s top three organic milk companies, Yili, Mengniu and Shengmu, they have perfect production, processing and transportation systems. Moreover, marketing and KOL strategy are are crucial to their success.
Consumer analyses of organic food in China
Customer preferences of organic food
According to a study conducted by International Trade Center of 204 Chinese organic consumers in Beijing and Shanghai, the top five reasons of choosing organic foods were:
1) Enforcement of quality
2) Overall quality
3) Certification relating quality
4) Food safety
5) Information about nutritional value
Issues that Chinese consumers were less concerned with were:
- Promotion and advertising of organic food
- Appearance
- Whether the organic food was produced in China
- The social status of people purchasing organic food
- The idea of face saving (mianzi) when purchasing organic food.
While consumers traditionally prefer to buy Chinese food, western lifestyles and eating habits are increasingly becoming the norm, especially among younger generations who have travelled overseas to study or work.
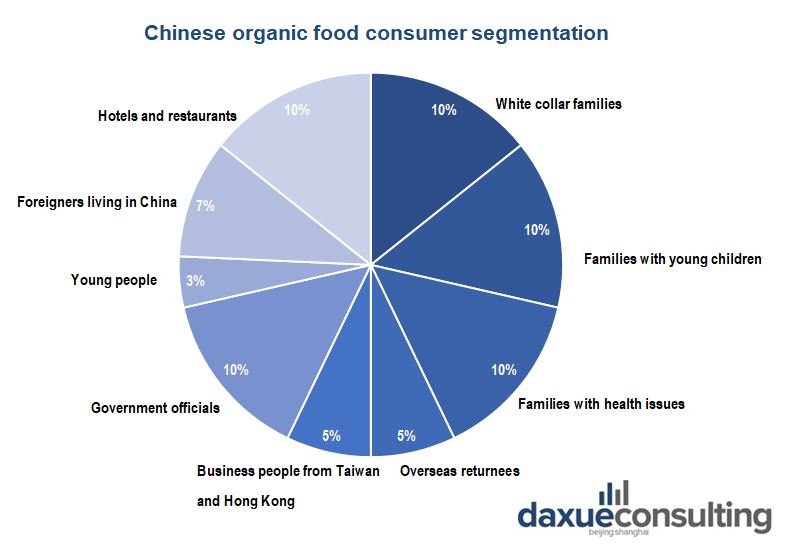
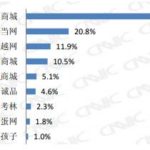
[Source: International Trade Center. The profile of different organic food consumers in China and their proportion in consuming]
Is organic food a necessity for Chinese consumers?
Most Chinese consumers are price sensitive and look for value when buying organic food. Are organic products safer than other products?Are foreign imports really worth paying 2-3 times the cost of domestic items?These are some questions Chinese consumers ask themselves when they buy organic food. For most Chinese consumers, they don’t think that organic food’s high price matches its nutritional value. And many consumers also consider organic food as a marketing term without real higher nutritional value. From a sustainability point of view, the organic food industry is not as friendly towards the environment as people imagined. The production of organic food also exhausts a large amount of carbon dioxide and occupies much more lands than traditional agriculture. It is obvious that organic food has more natural nutrients and secure guarantees, however most Chinese consumers consider it as a luxury.
Organic food trade in China, B2B
The industrial chain of organic food in China, B2B
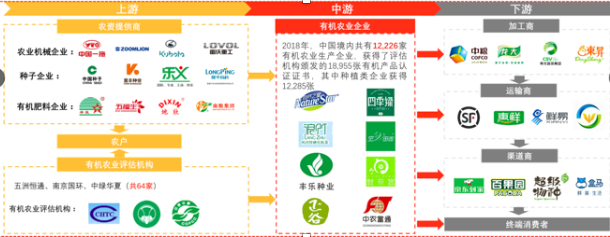
[Source: Leadleo research institute. The vertical structure of the organic food industry in China and its component companies.]
The upstream enterprises of the organic industry in China are mainly agricultural suppliers, farmers and organic assessment agencies. The midstream is comprised of organic agricultural enterprises. The downstream participants are transporters and distributors.
China is becoming one of the largest organic consumers in the world. With such potential, it’s not surprising that China has become a goldmine for international organic food suppliers. However, selling its products to Chinese consumers requires some adjustments and a specific strategy for cross-border e-commerce in China.
Retail e-commerce is an incredible impetus for China’s organic food industry
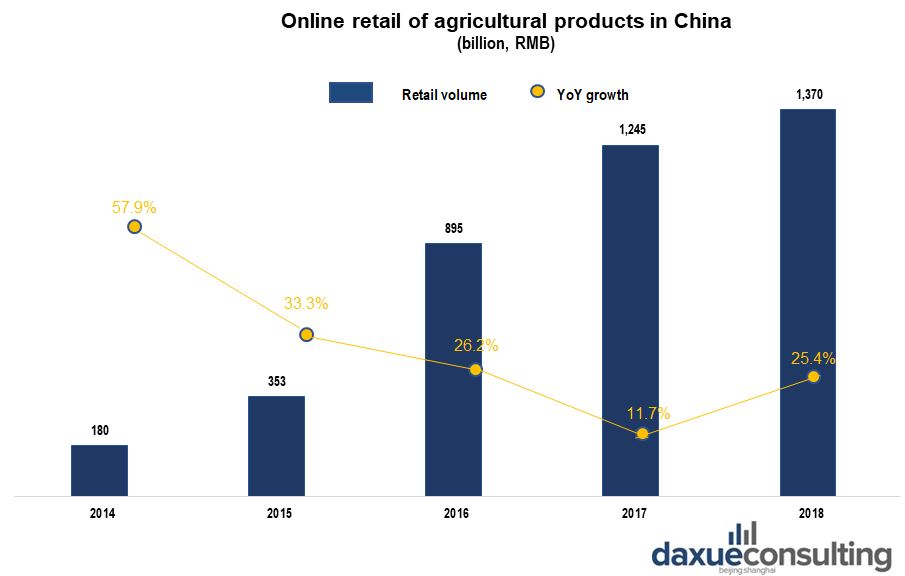
China is by far the largest e-retail market in the world. Thus, online retail and O2O models are the most efficient sales channels for organic food in China. In 2018, the amount of orders of Chinese online retailer Pinduoduo for agricultural products surpassed 65.3 billion RMB, with a 233% increase from 19.6 billion RMB in 2017. Hence, such a performance makes “Pinduoduo” the biggest Chinese online platform of agricultural products.
As the largest consumer market for organic packaged foods and beverages and the fastest growing organic food market in Asia, China’s organic market offers many opportunities for foreign B2B investors. However, it’s necessary to know what the are trends for B2B marketing in China and how to build a B2B sales network across China.
Imports and exports of organic food in China
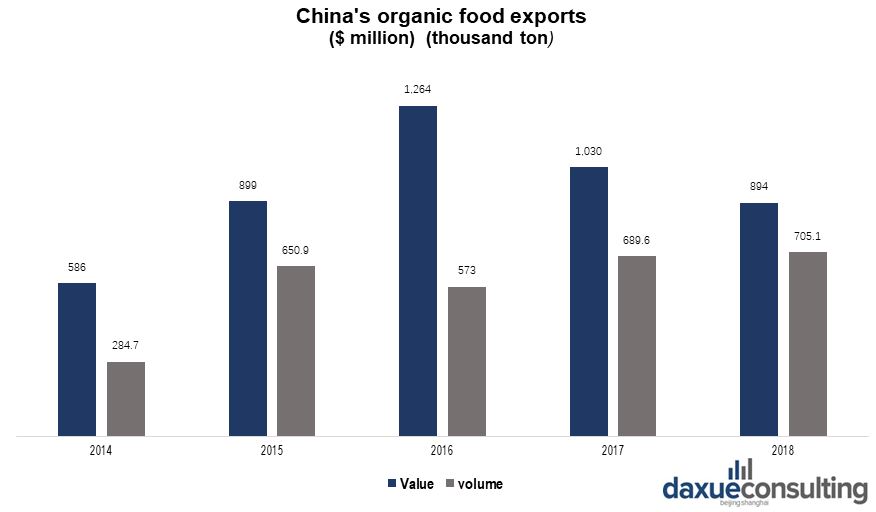
By 2018, food imports in China exceeded 424 billion RMB (US$60 billion). In addition, China is expected to be the top importer of foreign food, of which edible vegetable oils, cereal and milk products account for roughly half of all food imports. On the other hand, China’s organic food is mainly exported to Japan, America, Southeast Asia, The EU and South Korea, comprising 80% of China’s total exports. At present, China’s organic food exports only occupies a very small share of the international market, accounting for less than 1% of the global market share.
The impact of COVID-19 on the organic food market in China?
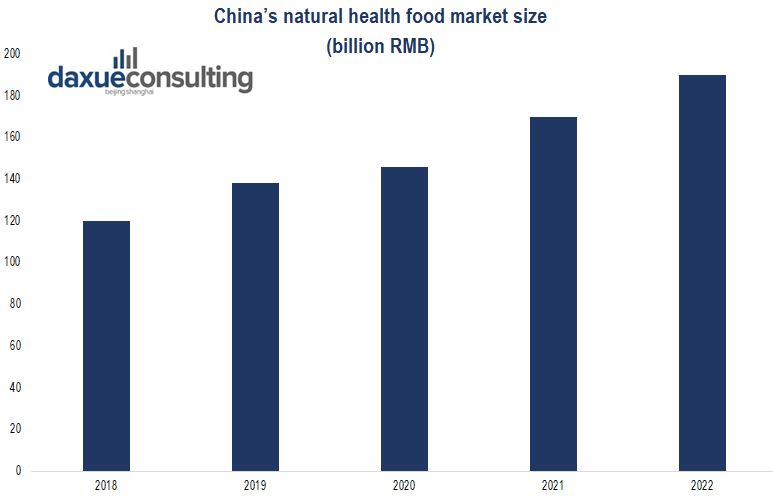
[Source: Zhihu. The evolution and forecast of China’s natural healthy food market.]
After the depression, the organic food market in China will quickly resume.
The impact of Covid-19 is like a bombing on China’s organic industry. Due to the recent situation, many of China’s food-trading firms have seen international orders fall by 75% because of foreign barriers to trade. Meanwhile, the country’s catering industry has been shut down, thus the demand for organic food has plummeted. Zhou Hong, president of one of China’s largest crop growers, estimated that the outbreak could reduce the company’s exports for 2020 by more than 20%. Nonetheless, after the outbreak, physical health has become the core of Chinese consumers’ priorities. As Chinese consumers’ incomes continue to rise and more are concerned with a healthy diet, the market size of natural health food is expected to approach 200 billion RMB in 2022. In light of this wave in health consciousness, some green food companies seized the opportunity. “Grain Mill” harvested 918 million RMB as the turnover and 105 million RMB for net profit of the 2th quarter in 2019, which turned it into the industry leader.
Covid-19’s impact on customer’s behavior in China
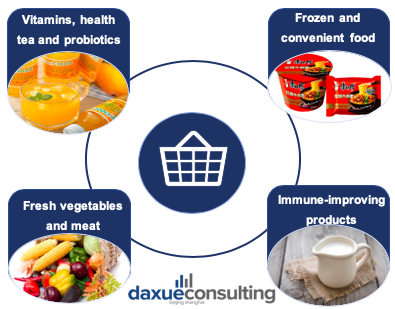
Due to many restrictions proposed by the Chinese government to minimize the impact of Covid-19, people have had to stay at home and cook by themselves. Thus, frozen and convenient foods became their first choice. According to research released by Nelson about how Asian consumers will eat post Covid-19, 86% of Mainlanders said they would eat at home more often than before the outbreak. In addition, 80% will pay more attention to a healthy diet and 89% claimed that they prefer to buy fresh food online now. On the other hand, health products such as vitamins, health teas and probiotics are also popular among Chinese consumers. As a result, the epidemic has changed many Chinese people’s consumption behaviors; and health-related products will be favored during and after the special period.
The Covid-19, a plight or booster for the organic milk industry in China?
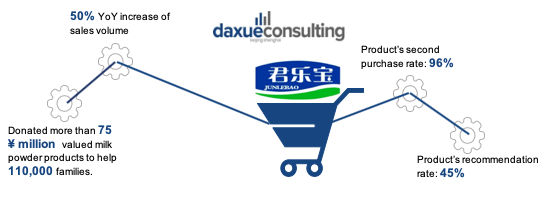
Although Chinese consumers have huge demand for organic milk, China’s milk industry will inevitably be impacted by Covid-19 on production, transportation and sales. Focusing on China’s biggest dairy company, “Yili” encountered a 10.7% contraction on its 1st quarter’s turnover compared with 2019. However, despite the liquid milk revenue of “Yili” plummeting by 19%, its market share rose by 1.1%, arriving at 39.3%. Organic milk contains various nutrients and can help improve people’s immune systems, which will help in producing a purchasing upsurge. Therefore, the sales of organic milk and milk powders by “Junlebao” rocketed by more than 50% during the outbreak. Meanwhile, It is interesting to know that the sales of milk powder by foreign brands make up 60%-65% of total national sales in China. And as for most dairy companies, they are very optimistic about the organic milk market in China after Covid-19.
Future of the Chinese organic food industry
China’s organic food market is developing rapidly, and the potential demand for organic food among Chinese consumers is enormous. As for the choice of organic food, imported organic food has quality advantage. Although Covid-19 has depressed China’s organic food industry, the emergence of a healthy diet concept and increasing demand for organic food will lead to a rapid recovery. Just as Jack Ma said: the next richest person in China will be in the health industry.
If you have any question or would like to discuss your interests in organic food market in China, do not hesitate to reach out to our project managers at dx@daxueconsulting.com to get all answers to your questions.
Listen to 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast