Smartphones in China: Giant Xiaomi is Building a Smart House “Ecosystem”
Xiaomi China was founded in April 2010 by Chinese serial entrepreneur Lei Jun. The company mainly focuses on developing and providing high-quality software, hardware, and Internet-related products at affordable prices. In November 2010, two months earlier than Tencent’s WeChat, Xiaomi launched the mobile messaging app MiTalk Messenger (“Miliao” in Chinese) and its operating system MIUI based on Android, and Mi Phones. Xiaomi phones range between 700rmb and 2400rmb, and they are at least 50% cheaper compared to Apple, and 40% cheaper than Samsung. With Mi phone’s advanced technology and very competitive price, the startup quickly became very popular and sold more than 160 million phones since its creation in the Chinese market. According to the website Digital Trends, the 6-year-old tech startup managed 14-percent growth last year, going from 61 million to 70 million sales. Xiaomi is one of the fastest-growing startup in the world and the second largest smartphones in China, behind Huawei with 100 million total sales.
Smartphones in China: Xiaomi aims to become an international smart home player
With the release of Xiaomi Box in 2013, Xiaomi started to move towards the smart house industry. Xiaomi has offered a series of high-end smart home devices at relatively low prices. All Xiaomi smart devices can be connected to the WIFI at home, and controlled by an App called Mijia. For example, with Mi box and Mijia app, customers can use their phone to watch the news, shows and videos, or play games. Xiaomi smart devices are not exclusive to any mobile phone operating systems but are mainly designed for MIUI and Mi router. Thanks to Mijia app, users can easily control all smart home appliances with their phone, as long as they have Internet access.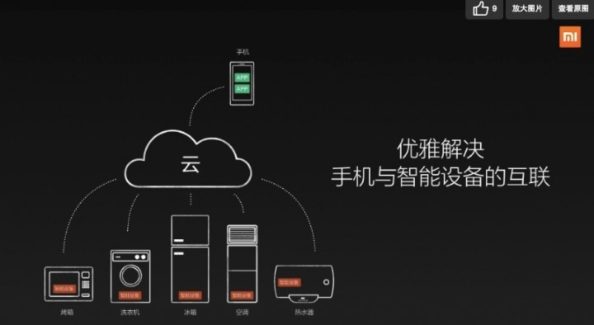
Xiaomi smart home devices examples
| Name of device | Release Date | Price (Chinese Yuan) |
| Mi router | 2013.11 | 79 – 699 |
| Mi television | 2014.05 | 1799 – 9999 |
| Mi home camera | 2014.10 | 149 |
| Mi air purifier | 2014.12 | 699 |
| Mi smart scale | 2015.03 | 99 |
| Mi Band 2 | 2016.06 | 149 |
| Mi water purifier | 2016.03 | 1999 |
| Mi Rice Cooker | 2016.03 | 999 |
| Mi Vacuum | 2016.09 | 1699 |
“Xiaomi is a smartphone company, but we are also an e-commerce company. Mi.com is the third-largest e-commerce site in China. An Internet services company, which even publishes games,” said Liu De, Xiaomi’s head of ecosystem products during an interview for Wired ( source: wired). Xiaomi is selling its accessories on its e-commerce platform Mi.com since April 2014 and in the showcase of its 22 Mi Home centres in mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. Among the 600 items sold by Xiaomi, the company makes only smartphones and tablets, TVs and set-top boxes, and routers. The rest is produced by 54 other start-ups in which Xiaomi has invested between $100,000 and $500,000, according to Liu De. This is what Liu calls the Xiaomi “ecosystem,” to create “a connected lifestyle.”
Xiaomi accelerates entering smart house industry by seeking alliances
 Xiaomi is highly sensitive to customer needs and market trends. For instance, it quickly developed Mi Air Purifier in 2014, in response to increasing air pollution concerns in China. Moreover, Xiaomi seeks to build strong relationships with traditional electronic manufacturers in China and to help them add new attributes to their existing products. In 2014, Xiaomi invested 1.26 billion RMB in local home-appliances maker Midea Group Co, and both parties have agreed to develop smart air conditioner. Midea Group is one of the most valuable and recognized electronics brands in China, known for affordable, high-quality consumer appliances and air conditioning systems.With this strategic alliance, Xiaomi can easily access Midea’s resources and capabilities, keep prices as low as possible and continue to provide devices at a competitive price.
Xiaomi is highly sensitive to customer needs and market trends. For instance, it quickly developed Mi Air Purifier in 2014, in response to increasing air pollution concerns in China. Moreover, Xiaomi seeks to build strong relationships with traditional electronic manufacturers in China and to help them add new attributes to their existing products. In 2014, Xiaomi invested 1.26 billion RMB in local home-appliances maker Midea Group Co, and both parties have agreed to develop smart air conditioner. Midea Group is one of the most valuable and recognized electronics brands in China, known for affordable, high-quality consumer appliances and air conditioning systems.With this strategic alliance, Xiaomi can easily access Midea’s resources and capabilities, keep prices as low as possible and continue to provide devices at a competitive price.
In the last five years, Xiaomi has accumulated a large number of loyal fans and Mi phone users. It helps Xiaomi sell smart devices online and develop mouth-to-mouth marketing. Beyond organic growth, Xiaomi also seeks strategic alliances and mergers. Lei Jun invested 60 million RMB to iKongjian, an O2O startup providing fast and cheap house decoration service, targeting Chinese millennials working in the major cities and who are too busy to decorate their houses by themselves. Xiaomi’s home appliances are bundled with the service. Furthermore, in 2014, Xiaomi cooperated with China Resource Land, a high-end estate company, and developed a smart house experience center in Haidian district, Beijing. All electronic devices, curtains, lighting system and security system were controlled by mobile phones.
Xiaomi’s vision: “Bring innovation to everyone.”
According to the Wall Street Journal, Xiaomi is the world’s most valuable tech startup. Although Xiaomi is a very successful smartphone business, Lei Jun’s ambition does not stop here. Xiaomi CEO’s final goal is to “bring innovation to everyone.” The smart home appliance is a foreseeable future for high tech companies. Global companies like Apple, Google and Amazon have already moved into this market. Huawei, Tencent, and Alibaba, also pay a very close eye on the industry. Compare to these companies, although Xiaomi is one of earliest players in China, it still faces severe competition. Once Xiaomi builds up its “Internet-enable ecosystem” successfully, it could potentially emerge as the biggest smart home player in the world.
Stay Updated! Follow us on Facebook: