Education elsewhere: China seeks out exchanges in other countries
China as a good source of international students
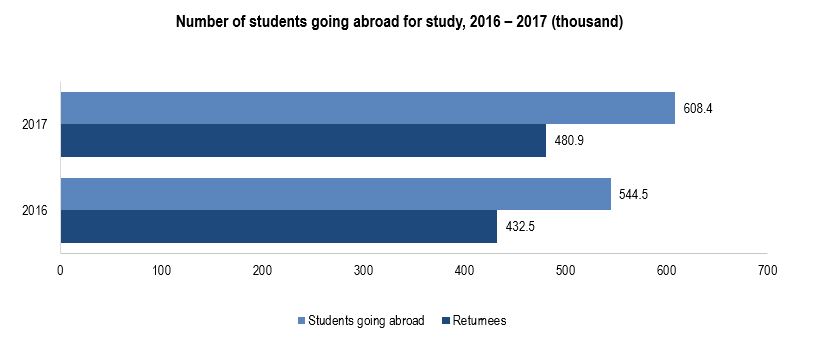
The number of students going abroad is mounting every year as increasing numbers of Chinese students are looking for an experience overseas. Between 2008 and 2016, the number of students studying abroad had increased from 179,800 to 544,500 showing overwhelming growth. In 2017 alone, 608,400 students left China for overseas study. This fast growth has been developing since 2010 and has been growing year on year. Today, China is the largest source of international students and is expected to grow. Yu Minhong, the founder and CEO of the New Oriental Education and Technology Group as well as a member of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference’s National Committee, estimates that the number of students studying abroad will peak at 700,000 to 800,000 each year. However, the coronavirus outbreak has caused Chinese students to re-evaluate their study abroad plans, gradually initiating a shift in destination preferences and post-grad decisions.
Why is China’s study abroad rate increasing?
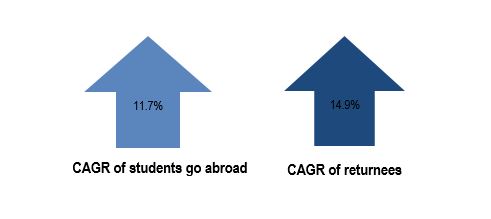
The price of student exchanges has also become increasingly more affordable as the booming economy has allowed more parents and students to meet these heavy costs. This has allowed more Chinese students the opportunity to go overseas in order to increase their chances of employment after graduation. This is especially important as 2010 brought a higher percentage of unemployed graduate students causing students to look for ways to differentiate themselves in the job market. Many students, however, despite the abroad experience often return home with the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) being 14.9% for returnees and 11.7% for students going abroad. This is as many students intend to go back after studying or find the job market overseas too difficult with them often having lower revenues. The government also offers incentives to returnees in China with them having better opportunities in larger cities which they would not have been able to access without foreign education.
Chinese students studying abroad: Destination preferences
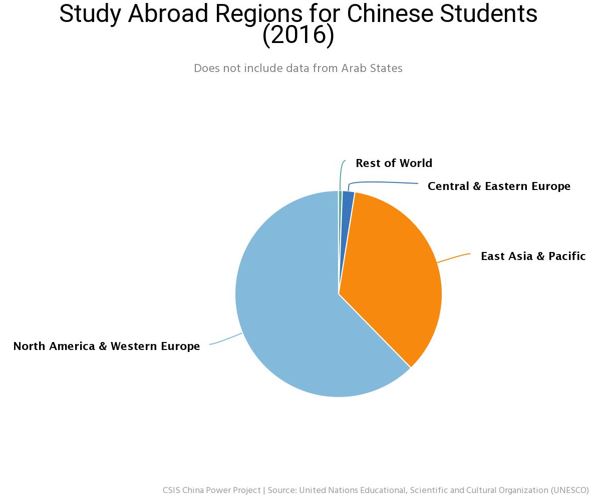
Due to China’s massive population, it sends more students abroad than any other country and this number is still rising. This is seen with growth in the number of returning Chinese students overtaking the number of students studying abroad in 2016. The United States (US), however, has been the preferred destination for many Chinese students with it remaining the top destination year on year. The quality of a US education is reputable and many Chinese students study in the US may hope to stay and live there after graduation in order to enjoy the lifestyle of a developed country. Further, many Chinese international students prefer to study in English speaking countries with the US, Australia and the UK making up approximately 60% of outbound students. China is also the largest source of international students in many countries with Chinese students accounting for 30% of students in America, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.
However, what may have been a popular destination could be fading due to the pandemic and various political clashes (such as trade war).
According to a report on the economic impacts of the pandemic published in April by the US-China Economic and Security Review Commission, a host of issues can reduce Chinese demand for higher education in the US in the following academic year. These include delays or cancellations of US entrance exams in China, travel restrictions, and the perpetuating uncertainty of when US college classes will be in-person. The economic impacts could be severe as nearly a third of all tuition payments to US public universities stem from international students. Also, cancelled university recruitment events in China and inability to work with local recruitment agencies could further contribute to the decrease in enrolment (learn more on how the coronavirus has impacted Chinese students’ study abroad decisions).
Prior to the coronavirus outbreak, there has already been a decline in enrolments from Chinese students in US schools, most of which are part of the larger picture of rising Sino-US political tensions. For instance, visa refusals have been a common problem facing Chinese students. As such, the development and job opportunities back home prove to be attractive reasons for the drop in Chinese students seeking to settle overseas after graduation, which was 85.4% in 2013 but 79.4% in 2016.

Other countries are also increasing their awareness in China as they gain market share slowly and Chinese students are ready to assess new destinations. It is clear, however, that English speaking countries have an added advantage to attract Chinese students who want to better their English speaking skills. Some regions have become more popular with East Asia and the Pacific taking a significant portion of Chinese students with the convenience of location. This is with Japan as the 4th most popular country and South Korea as the 6th most popular country in 2016. This is also with Chinese students accounting for 57.3% of international students in Japan and 49.3% of students in South Korea. Many students also studied in Hong Kong due to its proximity.
Why do Chinese students study overseas?
Chinese students abroad: Social, personal and professional benefits
When surveyed it was found that 82.5% of companies and employers give returnee employees privileged treatment. A CCG survey found that almost half of the Chinese students surveyed who studied abroad believed that they were more competitive than their peers who studied at domestic universities. This is proven true with 20% of companies promoting returnees faster and 17.5% preferring returnees for core positions and 50% of state-owned enterprises claiming that they welcome returnees into core positions. These figures alone show the importance employers place on abroad studies with these high percentages indicative of the professional benefits provided to those with an overseas degree.

Another benefit this provides for Chinese citizens the influence abroad education has on Hukou. Hukou is strict and complicated household registration system which also doubles as a domestic passport that regulates the Chinese population both socially and geographically. It determines factors such as where a person can live and work, where their children can go to school particularly so if they belong to a rural area and the social welfare benefits they can receive. Returnees from abroad studies get a more flexible Hukou transfer policy which helps them settle down in tier 1 cities and gives them more opportunities in terms of experience and salary. Further, preferential policies are also provided by the government to get returnees to start a business by providing grants and incentives such as free or discounted offices or tax-free cars. This is in order to attract Chinese talents back to China.
Besides the social and professional benefits provided by organizations and the government, there are personal benefits for Chinese students who go on exchange. This is evident as 64% of Chinese international students pursue abroad education in order to enrich their personal experience. This includes improvement of their English skills, the knowledge they gain of a different culture, overseas life experience and an international network. These benefits can be gained by any student studying overseas but English based exchanges are particularly beneficial for Chinese students who have been studying English throughout a school. This is as it gives students a chance to gain practical experience in a different environment that makes them more employable in the long run. Other than Chinese and Spanish, English is one of the most widespread languages in the world. It has gained increasing importance with English being an official language in at least quarter of the world, with 400 million people speaking English as their first language and 1 in 5 people being able to speak or understand some English. The role of English in China cannot be understated especially as it is integral for professionals to compete within the business environment. This is illustrated with parents understanding this importance as they start English education early in order for their children to start off more competitively, thereby spiking the demand for English teachers in China.

Another major benefit is also the waiving of the Gaokao entrance exam. Gaokao is the test undertaken by high school students in order to study at university and it is known worldwide for being an extremely difficult and stressful exam. The test has been said to determine the course of a student’s life and is the only way to enter university. The supply of university spots is also known for not meeting demand- making the pressure on high school students enormous. Those who previously did not anticipate abroad studies and those determined to study overseas do not need to pass Gaokao which takes a significant amount of stress off of students.
Chinese studying overseas: Criteria for students picking universities
As studying abroad is very important for students and parents a lot of thought goes into picking the university and country they will be studying at. A big determining factor to consider is the country itself. This requires evaluating the country itself by its size, population, economy and development degree. Chinese people prefer countries which are bigger and have a larger population, higher economic power and the development degree which makes the US the most popular country to go to. Some students are also concerned about the culture of the country itself.

Further, the school awareness in China that is the school’s brand reputation is very important. This is evident with 61% of students in a survey conducted by WSE choosing school reputation as the top consideration of school selection, with the success rate following at 48%, school location at 40% and expected income level after graduation being at 39%. This is as about 80% of international Chinese students go back to China after graduation which makes the school’s awareness and reputation important when considering job prospects in the future.
Moreover, the ranking itself is very important with many different versions of school rankings applying in China to help students and parents make decisions. This includes the QS World University Rankings and the Academic Ranking of World Universities and ranking in the top 100 is very beneficial to students wishing to return to China.
Additionally, the curriculum offered by the school itself is vital. This is with weight in decision making relating to the design of the curriculum, the composition of it, the availability of course choice, the quality and exclusivity of each course and even the internship opportunities that the school supports.
Lastly, whilst all of the above is extremely important, the cost is often a major determining factor. This includes the cost of tuition, living expenses and scholarships available. As such, many students go to Hong Kong for further study due to the lower expense and some European countries provide free public education for the same reason. This is evident with 45% of students being concerned about the cost of studying abroad, compared to only 27% of parents. Cost is especially important as 89% of students traveling abroad self-finance their study so they are very receptive to scholarships or less expensive locations.
International education: How do Chinese people look for information to choose the right university?
Chinese study abroad agencies and specialized education companies are important in helping students to pick countries and universities to study abroad at. They offer a broad range of services to students and help foreign universities and programs get more visibility among students. Due to the services offered, student’s families are willing to a pay a large amount of money for these services which include counseling services on programs, assistance in preparation, application and admission processes, test preparation, English classes as well as international study tours. The Beijing overseas service association also can help abroad institutions to select good partners among agencies to promote institutions in China.

Further, as stated, online information is very important with Chinese students spending a significant amount of time looking at the best destination, university ranking and application process. As such, a good online presence is essential for an overseas university- especially if it is not a top ranking one. Particularly, 31% of students depend on social media when researching for their study destination. They also look to the alumni network for recommendations and feedback as students trust advice from those who have attended the school itself. As such, it is important for universities to have good ambassadors as Chinese students want to hear about the university in a more personal and informal way.
Trends in types of study undertaken by Chinese students
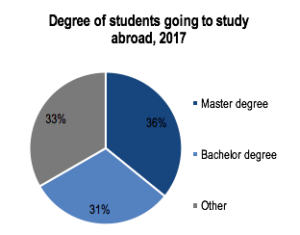
The types of study undertaken by Chinese students themselves vary with the type of study they undertake. This is with Master and Bachelor degrees at the forefront of reasons for going overseas for study, with other avenues collectively making up the remaining 31%. There is, however, a preference for longer study programs over shorter ones. This is with slower growth for shorter study options in comparison to the faster growth experienced by Bachelor and Masters degrees. This is as shorter exchanges are not as popular with Chinese students who prefer to spend the duration of their program overseas with four or two years being favored over a few months.
There are also trends evident in the degrees undertaken by Chinese students. This is with both engineering and business management as the most popular degrees chosen by students. However, in 2016 subjects shifted as more students paid attention to their own preferences over parental preferences and what is expected of them. This was evident as the Center for China & Globalization reported a decline in 2016 with students studying engineering, computer science and IT, math and statistics and social sciences, whilst the number of students who chose to study business management, foreign language and literature and education increased. Further, it was mentioned that subjects relating to business management, trade and corporate management and finance have increased as development in China has created more demand for professionals in these fields.
Market difficulty in China for student exchanges in lesser-known countries
Consulting agencies specializing in overseas programs still promote the US and other popular speaking countries such as the UK, Canada and Australia. As such, standing out from those countries can be quite challenging for smaller countries. This is as knowledge of the country studied at and a school’s ranking is very important for students. This is due to the implications it has for the employability of students, especially those wishing to return to China. Further, social recognition and prestige also play a role beyond professional necessity which can also be a determining factor for parents and students, especially from tier 1 cities.
Study abroad: The Belt and Road Initiative and its effect on Chinese international students

According to Forbes, the Belt and Road Initiative will affect 60% of the world’s population with the participation of 76 countries from Asia, Africa and Europe. The trade and infrastructure undertaking is thought to be one of the most ambitious undertakings in human history and is viewed as ‘a sort of 21st-century silk road’. Along with connecting through trade, Beijing currently offers 10,000 places each year for students who come from countries within the Belt and Road Initiative with China attracting more than 200,000 students from 64 of 68 Belt and Road countries in 2016. Further, since 2013 when the launch of the Belt and Road initiative took place, Chinese students have also flocked to Belt and Road countries with 24 educational agreements being signed between some of these countries since April 2017. This initiative opens up substantial and wide opportunities to educational bodies of countries within the initiative, with the Chinese government wanting to strengthen both educational and trade bonds between countries.
Opportunities for brands wanting to enter the Chinese market
Chinese students prefer English speaking countries in order to improve their English as it is a must-have skill in the work environment with 60% of Chinese students currently going abroad to the US, Australia and the UK. As a result, this increasing need for English helps leverage English speaking countries for exchanges as a whole – not just the top destinations sought by students. This is seen as Chinese students are now exploring new countries for overseas studies. There is, however, due to the Road and Belt Initiative, an opportunity for growth for many more educational organizations and countries to attract Chinese students using the initiative as leverage to strengthen the appeal for Chinese students. This is especially where educational organizations are not within the top 100 or are as well known to Chinese students. This awareness in China is particularly important as going abroad is meant to enhance employability and employment opportunities which cannot be achieved without businesses being aware of the educational organization. Further, an emphasis on the social and personal benefits students are looking for, along with strengthening programs in the more popular university courses, will help make organizations stand out to students. Most importantly, recognition by the Chinese Ministry of Education of the degree and the university itself is necessary for recognition and desirability among the Chinese.
Moreover, there are opportunities for educational organizations that are located in less expensive countries or areas should highlight their desirability and more expensive schools should offer scholarships in order to appeal to students who are self-financing their abroad study. However, it is also important to note that the urban middle classes are also estimated to increase; a McKinsey survey in 2015 found that there were 10 million affluent households with more than 300,000 RMB, and it is estimated to be 18 million by 2020. These households were mostly found in tier 1 to 3 cities but tier 4 to 5 cities were found to be steadily increasing their income. This growth in disposable income and wealth among cities is likely to have a positive effect is on expanding the number of students studying abroad and providing opportunities for more countries than in the past. Although there have been recent declines in Chinese students studying in the US as well as more returnees upon graduation, studying abroad is still a reflection of social mobility and status. The UK sits behind the US as a top destination, with pursuing a master’s degree as an attractive choice with its one-year program considering costs and study requirements. In the coming years, we may see a larger shift in the preference of university destinations among Chinese students in light of the recent events.
See how COVID-19 has impacted Chinese students’ aspirations to study and work abroad.
Author: Jessica Farrell
Daxue Consulting has conducted a series of surveys on Competitive Benchmarking in China and developed a specific framework to analyze the key insights related to your competition in China.
Competitive analysis is defined as identifying your competitors and evaluating their strategies to determine their strengths and weaknesses about those of your product or service. Daxue provides you with the tools needed to win in a market full of players.















